1 时间复杂度和排序算法
1.1 交换两个数的写法
1 2 3 4 5 public void static swap (int [] arr, int i, int j) { arr[i] = arr[i] ^ arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[i] ^ arr[j]; arr[i] = arr[i] ^ arr[j]; }
异或操作:
满足交换律和结合律。
第一行:
arr[i] = arr[i] ^ arr[j];arr[j] = arr[j];
第二行:
arr[i] = arr[i] ^ arr[j];arr[j] = arr[i] ^ arr[j] ^ arr[j] = arr[i];
第三行
arr[i] = arr[i] ^ arr[j] ^ arr[j] = arr[i] ^ arr[j] ^ arr[i] = arr[j];arr[j] = arr[i];
交换成功。
1.2 找到数组中出现奇数次的数字
1.2.1 假设只有一种数出现奇数次
根据异或操作的结果,如果数字出现偶数次异或完之后会变成0,奇数次的还是原来本身,最后将0和奇数次的数异或还是它本身。
1 a ^ b ^ c ^ a ^ b ^ b ^ a ^ a ^ c = b;
因此只有一种数的可以直接遍历所有数然后异或,最终结果就是答案。
1.2.2 假设有两种数出现奇数次
首先根据异或操作结果,遍历一遍后,所有偶数次的数都会抵消,只剩下两个奇数次的数的异或记为eor = a ^ b,这里eor不为0,因为a和b是两种数,肯定不相等,所以eor肯定不是0,所以可以在eor中找到至少一个二进制位为1,假设这个二进制位为第i位,那么在第i位中,a和b的值一定不相同。i位的不同将所有数划分为第i位是1的和0的。
第i
第i
others 0
others 1
a(或b)b(或a)
取另一个变量eorp遍历所有第i位是0或者1的,即可划分出a或者b。eorp的值肯定为a或者b。因为others 0或者others 1一定是偶数个,最终会抵消。eor ^ eorp可以得到另一个奇数次的数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public static void printOddTwiceNum (int [] arr) { int eor = 0 ; for (int cur : arr) { eor ^= cur; } int rightOne = eor & (~eor + 1 ); int eorp = 0 ; for (int cur : arr) { if ((cur & rightOne) == 0 ) { eorp ^= cur; } } }
上述代码中int rightOne = eor & (~eor + 1),这行代码作用是获取到从右往左第一个不为0的位置上的数,并且让其他位都为0。其中~eor + 1是eor的补码。eor = 10001010则~eor + 1 = 01110110异或后= 00000010。if ((cur & rightOne) == 0)这里的条件只能是== 0 \ != 0 \ == rightOne \ != rightOne。因为rightOne其他位都是0,只有某一位是1,所以异或后的结果,只有这一位是0或者1。
1.3 插入排序
插入排序思想:假设0 - i位置的数有序,从i + 1位置向前看,将i + 1位置的数插入到前边有序的数组中使0 - i + 1的数仍然有序。将i + 1的数依次与前一个数比较,如果小于前一个数就交换,然后再与前一个数比较,直到不小于前一个数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public static void insertionSort (int [] arr) { if (arr == null || arr.length < 2 ) { return ; } for (int i = 1 ; i < arr.length; i++) { for (int j = i - 1 ; j >= 0 && arr[j] > arr[j + 1 ]; j--) { swap(arr, j, j + 1 ); } } } public static void swap (int [] arr, int i, int j) { int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; }
这里的代码中将比较大小的条件放在了for循环中可以简化代码,同时要注意向前比较时下标不能越界。j指向的前一个数,j + 1指向当前的数,如果条件成立,即前一个数比当前的数大,就交换,交换后j--,然后下一次比较后j指向的仍然是前一个数,j + 1指向的仍然是当前的数。
1.4 Master公式
一个递归方法可以表示成如下的递推式:
1.5 归并排序
在数组中,每一个数的左边比当前数小的数累加起来,叫做这个数组的小和。例如[1, 3, 2, 4],1左边没有比当前数小的;3左边有,是1;2左边有,是1;4左边有,是1
3
2,将这些所有加起来,即为小和。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 public static void mergeSort (int [] arr) { if (arr == null || arr.length < 2 ) { return ; } mergeSort(arr, 0 , arr.length - 1 ); } public static void mergeSort (int [] arr, int left, int right) { if (left >= right) { return ; } int [] t = new int [right - left + 1 ]; int mid = left + (right - left) / 2 ; mergeSort(arr, left, mid); mergeSort(arr, mid + 1 , right); int i = left, j = mid + 1 , k = 0 ; while (i <= mid && j <= right) { if (arr[i] <= arr[j]) { t[k++] = arr[i++]; } else { t[k++] = arr[j++]; } } while (i <= mid) { t[k++] = arr[i++]; } while (j <= right) { t[k++] = arr[j++]; } for (i = left, k = 0 ; i <= right; i++, k++) { arr[i] = t[k]; } }
同时需要转变一下思路,如果这个数的右边有比当前数大的数,那么当前数就会被加起来。left = [1, 2, 2, 4]和right = [2, 3, 5]合并时,left[0] < right[0],可以肯定,right数组中所有的数都比left[0]大,那么right这些数计算时都会加上left[0],因此left[0]会被计算right.length - 0次。left[1] = right[0]时,和普通归并排序的合并过程略有不同,这里需要首先合并right数组,因为如果首先合并left数组,想要找到right数组中比left[1]大的数不太容易了,而首先合并right数组的话,可以让right的下标跳出相等的限制,当right的数比left[1]大,就可以找到有多少数比left[1]大,就可以求出小和。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public int smallSum (int [] arr) { if (arr == null || arr.length < 2 ) { return -1 ; } return mergeSort(arr, 0 , arr.length - 1 ); } private int mergeSort (int [] arr, int left, int right) { if (left >= right) { return 0 ; } int mid = left + (right - left) / 2 ; int ret = mergeSort(arr, left, mid) + mergeSort(arr, mid + 1 , right); int i = left, j = mid + 1 ; int k = 0 ; int [] t = new int [right - left + 1 ]; while (i <= mid && j <= right) { if (arr[i] < arr[j]) { ret += arr[i] * (right - j + 1 ); t[k++] = arr[i++]; } else { t[k++] = arr[j++]; } } while (i <= mid) { t[k++] = arr[i++]; } while (j <= right) { t[k++] = arr[j++]; } for (i = left, k = 0 ; i <= right; i++, k++) { arr[i] = t[k]; } return ret; }
力扣 逆序对问题。同样利用归并排序的过程,在归并过程中判断逆序对的数量。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public static int reversePairs (int [] arr) { if (arr == null || arr.length < 2 ) { return 0 ; } return reversePairs(arr, 0 , arr.length - 1 ); } public static int reversePairs (int [] arr, int left, int right) { if (left >= right) { return 0 ; } int mid = left + (right - left) / 2 ; int ret = reversePairs(arr, left, mid) + reversePairs(arr, mid + 1 , right); int [] t = new int [right - left + 1 ]; int i = left, j = mid + 1 , k = 0 ; while (i <= mid && j <= right) { if (arr[i] <= arr[j]) { t[k++] = arr[i++]; } else { t[k++] = arr[j++]; ret += mid - i + 1 ; } } while (i <= mid) { t[k++] = arr[i++]; } while (j <= right) { t[k++] = arr[j++]; } for (i = left, k = 0 ; i <= right; i++, k++) { arr[i] = t[k]; } return ret; }
1.6 快速排序
这里采用三路排序,选取一个分界值x,然后划分出小于x的,等于x的,大于x的。然后分别对小于x的和大于x的排序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public static void quickSort (int [] arr, int left, int right) { if (left >= right) { return ; } int x = arr[left + (int ) (Math.random() * (right - left + 1 ))]; int less = left - 1 ; int i = left; int more = right + 1 ; while (i < more) { if (arr[i] < x) { swap(arr, i++, ++less); } else if (arr[i] > x) { swap(arr, i, --more); } else { i++; } } quickSort(arr, left, less); quickSort(arr, more, right); } private static void swap (int [] arr, int i, int j) { int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution {public : vector<int > sortArray (vector<int >& nums) { quick_sort (nums, 0 , nums.size () - 1 ); return nums; } default_random_engine e; void quick_sort (vector<int > &arr, int left, int right) if (left >= right) { return ; } int x = arr[e () % (right - left + 1 ) + left]; int less = left - 1 , more = right + 1 , i = left; while (i < more) { if (arr[i] < x) { swap (arr[++less], arr[i++]); } else if (arr[i] > x) { swap (arr[--more], arr[i]); } else { i++; } } quick_sort (arr, left, less); quick_sort (arr, more, right); } };
1.7 堆
大根堆示例如下:
以大根堆为例,主要实现两种操作:
插入数据,在最后插入数据,然后依次向上操作,比较当前数和父节点的大小,如果大于父节点,则进行交换,然后父节点再和它的父节点比较。
1
删除数据,如删除根节点的数据,可以将最后一个数覆盖掉根节点的数,然后向下操作。找到两个孩子(如果有)的最大值,和父节点进行比较,如果大于父节点,则交换,然后再从这个节点向下操作。
代码实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 public static void heapInsert (int [] arr, int index) { while (arr[index] > arr[(index - 1 ) / 2 ]) { swap(arr, index, (index - 1 ) / 2 ); index = (index - 1 ) / 2 ; } } public static void heapify (int [] arr, int index, int heapSize) { int left = 2 * index + 1 ; while (left < heapSize) { int largest = left + 1 < heapSize && arr[left + 1 ] > arr[left] ? left + 1 : left; largest = arr[largest] > arr[index] ? largest : index; if (index == largest) { break ; } swap(arr, index, largest); index = largest; left = 2 * index + 1 ; } } public static void heapify (int [] arr, int index, int heapSize) { int t = index, left = 2 * index + 1 , right = 2 * index + 2 ; if (left < heapSize && arr[left] > arr[t]) { t = left; } if (right < heapSize && arr[right] > arr[t]) { t = right; } if (t != index) { swap(arr, index, t); heapify(arr, t, heapSize); } }
如果要删除堆中的第一个元素也就是根节点,可以直接使用heapify方法,index设为0即可,但这个方法也支持从其他位置向下堆化操作。如果想要删除任意位置的元素:
将末尾的值覆盖掉要删除的元素的值。
基于当前位置进行向上或向下操作。
如果覆盖的值比原值大,则向上操作。
否则向下操作。
但是可以不必进行判断操作,因为在向上向下操作时,会首先判断是否满足条件,因此可以直接执行一次向上和向下操作即可。
堆的应用
1.8 堆排序扩展题
首先给前k+1个数放入小根堆中,那么小根堆的堆顶必然是所有的最小值。因为题目中说移动距离不超过k,那么最小值所在的位置最远是在索引k的位置。取出最小值放入数组,然后往后加入一个元素,选出第二个小的元素,依此类推。具体实现中可以手写堆,也可以使用优先队列。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public static void sortedLessK (int [] arr, int k) { PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue <>(); int index = 0 ; for (; index <= Math.min(arr.length, k); index++) { heap.add(arr[index]); } int i = 0 ; for (; index < arr.length; index++, i++) { arr[i] = heap.poll(); heap.add(arr[index]); } while (!heap.isEmpty()) { arr[i++] = heap.poll(); } }
1.9 基数排序
待更新...
2 链表
2.1 回文链表的判断
回文链表
方法一
使用栈数据结构,遍历链表压栈,再依次出栈和原链表对比。O(N)
方法二
快慢指针,快指针走到结尾时,慢指针走到中间,慢指针继续向下遍历,遍历过程反转后边的链表,最后从开始和结尾依次向中间遍历,比对。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 class Solution { public boolean isPalindrome (ListNode head) { if (head == null ) { return true ; } ListNode fast = head, slow = head; while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null ) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; } slow = slow.next; ListNode tempSlow = reverse(slow); fast = tempSlow; slow = head; while (fast != null ) { if (slow.val != fast.val) { return false ; } fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } reverse(tempSlow); return true ; } public ListNode reverse (ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null , cur = head; while (cur != null ) { ListNode next = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = next; } return pre; } }
2.2 随机链表的复制
LCR
154. 复杂链表的复制 - 力扣(LeetCode)
方法一
使用哈希表,保存旧节点和新节点的键值对,然后遍历链表,将节点的下一个节点和随机节点复制。O(N)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public Node copyRandomList (Node head) { if (head == null ) { return null ; } Map<Node, Node> hash = new HashMap <>(); Node temp = head; while (temp != null ) { Node copy = new Node (temp.val); hash.put(temp, copy); temp = temp.next; } temp = head; while (temp != null ) { hash.get(temp).next = hash.get(temp.next); hash.get(temp).random = hash.get(temp.random); temp = temp.next; } return hash.get(head); }
方法二
首先遍历链表,遍历过程中复制当前节点,然后将复制的节点加入到链表中的当前节点后,直到复制完所有节点。next指针有值,而random指针没有值,下一步在这个新链表上操作,将复制的节点的random连接到正确的节点上。因为每一个旧节点a的下一个一定是复制的节点a_copy,所以旧节点a的random指针指向的节点a_random的下一个节点a_random_copy(即复制的节点)就是a_copy的random指针应该指向的节点。如图蓝色的箭头即为复制的节点的random指针的正确指向。注意 :random指针可能指向null,此时需要进行判空操作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class Solution { public Node copyRandomList (Node head) { if (head == null ) { return null ; } Node temp = head; while (temp != null ) { Node copy = new Node (temp.val); copy.next = temp.next; temp.next = copy; temp = temp.next.next; } temp = head; while (temp != null ) { Node copy = temp.next; copy.random = temp.random == null ? null : temp.random.next; temp = temp.next.next; } temp = head; Node headcopy = head.next; while (temp != null ) { Node copy = temp.next; temp.next = copy.next; temp = temp.next; copy.next = temp == null ? null : temp.next; } return headcopy; } }
2.3
判断一个链表是否有环,以及返回入环节点
环形链表I 环形链表II
方法一
使用哈希表,遍历整个链表,依次存入链表,存入之前判断是否已经存在,如果存在则当前链表为入环的第一个节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public ListNode detectCycle (ListNode head) { if (head == null ) { return null ; } Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet <>(); ListNode temp = head; while (temp != null && !set.contains(temp)) { set.add(temp); temp = temp.next; } return temp; }
方法二
快慢指针,快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,如果快指针遇到null则无环,否则当快慢指针相遇时有环,此时让快指针从头节点开始一次一步,慢指针一次一步,当快慢指针再次相遇时,该节点为入环的第一个节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public class Solution { public boolean hasCycle (ListNode head) { if (head == null ) { return false ; } ListNode fast = head, slow = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (fast == slow) { return true ; } } return false ; } public ListNode first (ListNode head, ListNode pos) { while (head != pos) { head = head.next; pos = pos.next; } return head; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 if (head == null ) { return null ; } ListNode fast = head, slow = head;while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null ) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (fast == slow) { fast = head; while (fast != slow) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } return slow; } } return null ;
2.4 判断两个链表是否相交
这里认为链表都是单链表
情况1:两个链表都无环面试题
02.07. 链表相交 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { if (headA == null || headB == null ) { return null ; } ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB; while (pA != pB) { pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next; pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next; } return pA; } }
❗注意 :判断是否为null时,使用的是pA当前指针,而不是pA.next,如果使用pA.next来判断,当不相交时,会发生无限循环的情况,pA和pB会一直不相等(也不为null)。所以使用pA当前指针。可以理解为,把最后链表结束时指向的null指针也算作一个节点,然后两个链表不相交时,最后都会指向null节点,那么两个链表就在null节点“相交”了,如下图所示。
情况2:一个有环一个无环(一定不相交)next指针,这不满足单链表。所以一定不相交。
情况3:两个都有环
不相交
在非环处相交
在环处相交
相交只有两种情况
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 if (circleNode1 == circleNode2) { return true ; } Node temp = circleNode2.next;while (temp != circleNode2) { if (temp == circleNode1) return true ; temp = temp.next; } return false ;
所以所有情况如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 public static ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { ListNode cycleNodeA = hasCycle(headA); ListNode cycleNodeB = hasCycle(headB); if (cycleNodeA == cycleNodeB) { return getIntersectionNodeNoLoop(headA, headB, cycleNodeA); } if (cycleNodeA == null || cycleNodeB == null ) { return null ; } ListNode temp = cycleNodeA; while (temp != cycleNodeB) { temp = temp.next; if (temp == cycleNodeA) { return null ; } } return cycleNodeA; } public static ListNode hasCycle (ListNode head) { if (head == null ) { return null ; } ListNode slow = head, fast = head; while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null ) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (fast == slow) { fast = head; while (fast != slow) { fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } return fast; } } return null ; } public static ListNode getIntersectionNodeNoLoop (ListNode headA, ListNode headB, ListNode endNode) { ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB; while (pA != pB) { pA = pA == endNode ? headB : pA.next; pB = pB == endNode ? headA : pB.next; } return pA; }
2.5 找到两个有序链表相同的节点
2.6
把链表按某个值分为小于 等于 大于的部分
排序链表
入门做法
把链表每个节点(不是值,是节点Node) 放在数组里,然后使用快排中的partition。
高级做法
首先准备6个指针,分别表示:
smallHead
小于部分的头指针
smallTail
小于部分的尾指针
equalHead
等于部分的头指针
equalTail
等于部分的尾指针
bigHead
大于部分的头指针
bigTail
大于部分的尾指针
使用这六个指针分别串联出小于部分 、等于部分 、大于部分 的链表。小于部分 的链表中,也就是利用尾插法插入到以smallHead为头结点的链表的末尾,等于、大于的节点同理。注意 :可能不存在小于部分 或者等于部分 等等,要对每个进行判空处理,防止出现空指针异常。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 public static ListNode listPartition (ListNode head, int pivot) { PartitionNode small = new PartitionNode (); PartitionNode equal = new PartitionNode (); PartitionNode big = new PartitionNode (); ListNode temp = head; while (temp != null ) { if (temp.val < pivot) { small.insertTail(temp); } else if (temp.val > pivot) { big.insertTail(temp); } else { equal.insertTail(temp); } temp = temp.next; } if (small.head != null ) { if (equal.head != null ) { small.tail.next = equal.head; equal.tail.next = big.head; } else { small.tail.next = big.head; } return small.head; } else if (equal.head != null ) { equal.tail.next = big.head; return equal.head; } return big.head; } static class PartitionNode { ListNode head, tail; void insertTail (ListNode node) { if (head == null ) { head = tail = node; } else { tail.next = node; tail = node; } } } static class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; public ListNode (int val) { this .val = val; this .next = null ; } }
链表快速排序
由此引出对链表的快速排序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 public static PartitionNode quickSortList (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null ) { return new PartitionNode (head, head); } ListNode pivotNode; ListNode slow = head, fast = head; while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null ) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } pivotNode = slow; PartitionNode small = new PartitionNode (); PartitionNode equal = new PartitionNode (); PartitionNode big = new PartitionNode (); ListNode temp = head; while (temp != null ) { if (temp.val < pivotNode.val) { small.insertTail(temp); } else if (temp.val > pivotNode.val) { big.insertTail(temp); } else { equal.insertTail(temp); } temp = temp.next; } if (small.head != null ) { small.tail.next = null ; } if (equal.head != null ) { equal.tail.next = null ; } if (big.head != null ) { big.tail.next = null ; } small = quickSortList(small.head); big = quickSortList(big.head); if (small.head != null ) { if (equal.head != null ) { small.tail.next = equal.head; small.tail = equal.tail; equal.tail.next = big.head; } else { small.tail.next = big.head; } small.tail = big.tail == null ? small.tail : big.tail; return small; } else if (equal.head != null ) { equal.tail.next = big.head; equal.tail = big.tail == null ? equal.tail : big.tail; return equal; } return big; } class PartitionNode { ListNode head, tail; void insertTail (ListNode node) { if (head == null ) { head = tail = node; } else { tail.next = node; tail = node; } } public PartitionNode () { } public PartitionNode (ListNode head, ListNode tail) { this .head = head; this .tail = tail; } } class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; public ListNode (int val) { this .val = val; this .next = null ; } }
链表归并排序
对于链表的排序,使用归并排序是更好的选择,可以采用更少的代码完成,同时可以使用迭代的方式优化排序,使空间复杂度O(logn)优化为O(1)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public static ListNode mergeSort (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null ) { return head; } ListNode fast = head, slow = head; while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null ) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } ListNode mid = slow.next; slow.next = null ; ListNode left = mergeSort(head); ListNode right = mergeSort(mid); ListNode ret = new ListNode (0 ); ListNode tail = ret; while (left != null && right != null ) { if (left.val <= right.val) { tail.next = left; left = left.next; } else { tail.next = right; right = right.next; } tail = tail.next; } tail.next = left == null ? right : left; return ret.next; }
❗空间复杂度O(1)的待更新
3 二叉树
3.1 遍历
递归、非递归的前中后序遍历要会写。
3.1.1 前中后序遍历(非递归)
前序遍历
首先设置一个栈结构用于存储。整体遍历流程如下:注意 :加入孩子节点时一定是先加入右孩子,再加入左孩子,因为栈是后进先出的顺序,所以要后加入左孩子。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public static void preOrderUnRecur (Tree root) { if (root == null ) { return ; } Stack<Tree> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { Tree pop = stack.pop(); System.out.print(pop.val + " " ); if (pop.right != null ) { stack.push(pop.right); } if (pop.left != null ) { stack.push(pop.left); } } System.out.println(); }
后序遍历
前序遍历的顺序是:根左右,后序遍历的顺序是:左右根。假设现在有前序'(前序撇)遍历:根右左,那么将这个前序'遍历的顺序加入到另一个栈中,最后统一输出,根据栈的现先进后出顺序,那么输出的结果是:左右根。这就是后序遍历的做法。注意 :前序遍历时保证根左右的顺序,加入子孩子时先加入的右孩子,而现在需要根据前序遍历得到前序'遍历即根右左的顺序,因此需要先加入左孩子。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public static void postOrderUnRecur (Tree root) { if (root == null ) { return ; } Stack<Tree> stack1 = new Stack <>(); Stack<Tree> stack2 = new Stack <>(); stack1.push(root); while (!stack1.isEmpty()) { Tree pop = stack1.pop(); stack2.push(pop); if (pop.left != null ) { stack1.push(pop.left); } if (pop.right != null ) { stack1.push(pop.right); } } while (!stack2.isEmpty()) { System.out.print(stack2.pop().val + " " ); } System.out.println(); }
中序遍历
中序遍历顺序:左根右。算法流程:
如果左孩子不为空,压栈,将新压入的节点设置为“当前节点”继续执行a
如果左孩子为空,弹出栈,打印
将弹出栈的节点的右孩子设置为“当前节点”,继续执行a
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public static void midOrderUnRecur (Tree root) { if (root == null ) { return ; } Stack<Tree> stack = new Stack <>(); Tree temp = root; while (!stack.isEmpty() || temp != null ) { while (temp != null ) { stack.push(temp); temp = temp.left; } temp = stack.pop(); System.out.print(temp.val + " " ); temp = temp.right; } System.out.println(); }
❗中序遍历和前边的前序后序遍历代码区别较大,增加了一个指针指向当前遍历到了哪个节点,而且while循环条件中的temp != null是必需的,因为当栈空的时候,指针可能指向了根节点的右孩子,此时还没有遍历完,需要这个条件,防止丢失数据。
3.1.2 层序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public static void levelOrder (Tree root) { if (root == null ) { return ; } Queue<Tree> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Tree remove = queue.remove(); System.out.print(remove.val + " " ); if (remove.left != null ) { queue.add(remove.left); } if (remove.right != null ) { queue.add(remove.right); } } System.out.println(); }
3.2
求二叉树一层最多的节点个数(每一层的节点个数)
LeetCode
102
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public static int getMaxLevelNodes (Tree root) { Queue<Tree> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.add(root); int maxCnt = 0 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int size = queue.size(); maxCnt = Math.max(maxCnt, size); for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) { Tree remove = queue.remove(); if (remove.left != null ) { queue.add(remove.left); } if (remove.right != null ) { queue.add(remove.right); } } } return maxCnt; }
3.3 二叉树的最大宽度
二叉树最大宽度 null节点的数量,可以按照完全二叉树对数进行编号,然后使用最右端的非空节点索引减去最左端非空节点的索引+1即可得到这一层的宽度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 static class Pair <T, V> { T key; V value; public Pair (T key, V value) { this .key = key; this .value = value; } } public static int widthOfBinaryTree (Tree root) { if (root == null ) { return 0 ; } Queue<Pair<Tree, Integer>> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.add(new Pair <>(root, 0 )); int maxCnt = 0 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int size = queue.size(); int minIndex = Integer.MAX_VALUE, maxIndex = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) { Pair<Tree, Integer> pair = queue.remove(); Tree node = pair.key; Integer index = pair.value; minIndex = Math.min(minIndex, index); maxIndex = Math.max(maxIndex, index); if (node.left != null ) { queue.add(new Pair <>(node.left, 2 * index + 1 )); } if (node.right != null ) { queue.add(new Pair <>(node.right, 2 * index + 2 )); } } maxCnt = Math.max(maxCnt, maxIndex - minIndex + 1 ); } return maxCnt; }
3.4 判断是否是完全二叉树
LeetCode
958 方法1: 分两种情况:
对于任一个节点,如果有右孩子但无左孩子,直接返回false
在条件1不违反的条件下,如果遇到了第一个左右孩子不全的,如只有左孩子或者没有孩子,那么之后的节点必须全部是叶节点。
☆方法2: 层序遍历时将为null的节点也加入进去,如果出现null后,后续出现的节点都要是null否则就不是完全二叉树。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public boolean isCompleteTree (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return true ; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.add(root); boolean flag = false ; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = queue.remove(); if (node == null ) { flag = true ; } else { if (flag) { return false ; } queue.add(node.left); queue.add(node.right); } } return true ; }
3.5 判断满二叉树
满二叉树的特征:
每一层的节点个数=从 开 始
按照完全二叉树的索引编号,最后一个节点的编号为:从 开 始
本题从每一层节点个数判断,从3.2
求二叉树一层最多的节点个数 复用代码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public static boolean isFullBiTree (Tree root) { if (root == null ) { return true ; } int height = 0 ; Queue<Tree> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int size = queue.size(); if (size != Math.pow(2 , height)) { return false ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) { Tree node = queue.remove(); if (node.left != null ) { queue.add(node.left); } if (node.right != null ) { queue.add(node.right); } } height++; } return true ; }
3.6 判断平衡二叉树
LeetCode
110
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public boolean isBalanced (TreeNode root) { return getHeight(root) >= 0 ; } public int getHeight (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return 0 ; } int leftHeight = getHeight(root.left); int rightHeight = getHeight(root.right); if (leftHeight == -1 || rightHeight == -1 || Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1 ) { return -1 ; } return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1 ; } }
3.7 判断是否是二叉搜索树
LeetCode
98
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 private long pre = Long.MIN_VALUE;public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return true ; } boolean left = isValidBST(root.left); if (!left) { return false ; } if (pre >= root.val) { return false ; } pre = root.val; return isValidBST(root.right); }
3.8
找到二叉树两个节点的最低公共祖先节点
LeetCode
236 236.
二叉树的最近公共祖先 -
力扣(LeetCode)题解 null或者p``q直接返回。否则遍历左右子树。分别获取到左右子树的返回值。
如果左子树返回空,说明左子树肯定不存在p``q,直接返回right因为必然存在在right中。
如果左子树返回不空右子树返回空,则说明肯定存在在左子树中,返回left。
如果都不空,说明左右子树都存在分别存在p``q,则当前root为公共祖先,返回当前的root为公共祖先。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (root == null || root == p || root == q) { return root; } TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q); TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q); if (left == null ) { return right; } if (right == null ) { return left; } return root; }
3.9 二叉搜索树的中序后继
LeetCode
053 6.
图_哔哩哔哩_bilibili (二叉树的中序后继),二叉搜索树可看作是特殊情况
如上图,第一种情况的后续节点是e,第二种后续节点是b,第三种后续节点是a。针对情况2和3即待查找节点p没有右子树的情况下:
如果p在根节点的左子树中,那么根节点可能就是p的后续节点,后续节点也可能是根节点的左子树中。
如果p在根节点的右子树中,那么根节点就不是p的后续节点
那么怎么判断p在根节点的左子树还是右子树呢?这就用到了二叉搜索树的性质,如果p节点的值比根节点小那么p就在根节点左子树中,否则在右子树。
首先判断有没有右子树,如果有则直接找到右子树最左端节点返回。如果没有则执行下边操作
从根节点开始遍历,依次和p比较,判断p在根节点的哪个子树中
如果在左子树中,更新保存答案的变量,继续左子树
如果在右子树中,不更新,直接遍历右子树
直接遍历到最后为null
返回结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public TreeNode inorderSuccessor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p) { if (root == null ) { return null ; } if (p.right != null ) { TreeNode temp = p.right; while (temp.left != null ) { temp = temp.left; } return temp; } TreeNode temp = root; TreeNode ret = null ; while (temp != null ) { if (temp.val <= p.val) { temp = temp.right; } else { ret = temp; temp = temp.left; } } return ret; }
3.10 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
B站视频
3.11 判断是否是二叉树
给定n个节点和m条有向边,节点从[0, n - 1]表示,m条边使用(a,
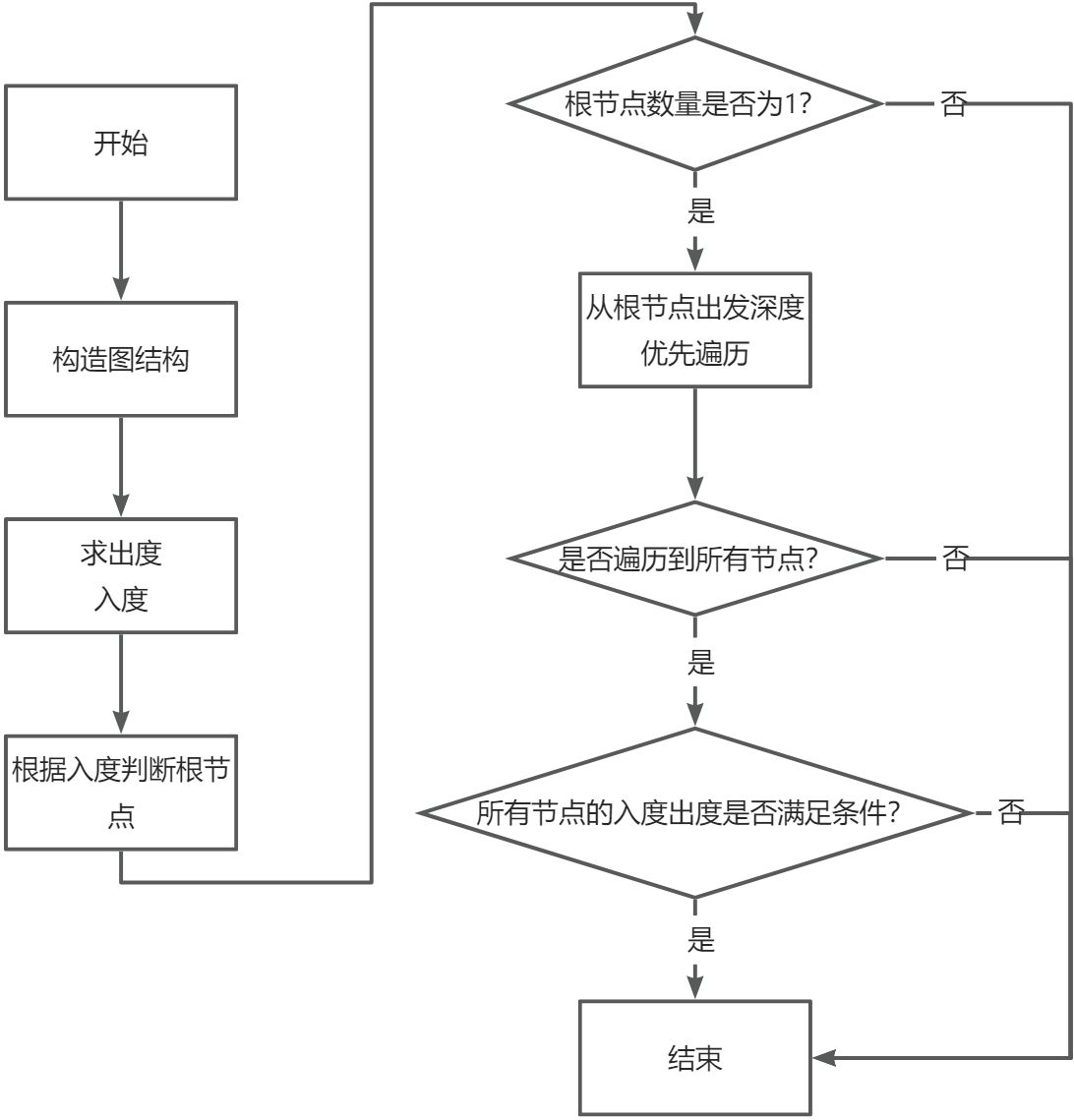
b)的数对(a指向b)表示为b的父节点是a。判断给定的结果是不是二叉树。有向图 ,除根节点外每个节点的入度为1 、出度小于等于2 ,根节点的入度必须为0 、出度小于等于2 且只有一个根节点 ,同时保证从根节点出发可以遍历到所有的节点 。
正确
出度不满足条件
入度不满足条件
树中存在父子节点之间“互为父子”,则可以从出入度判断不满足条件
根节点个数大于1
从出入度判断,只有一个入度为0的节点,所以无法从入度为0的个数判断图是否连通,需要使用dfs遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 void dfs (vector<vector<int >> &g, int t, bool *st) st[t] = true ; for (int i = 0 ; i < g[t].size (); i++) { if (!st[g[t][i]]) { dfs (g, g[t][i], st); } } } bool isBinaryTree (int n, vector<pair<int , int >> &edges) vector<vector<int >> g (n, vector <int >()); for (int i = 0 ; i < edges.size (); i++) { g[edges[i].first].push_back (edges[i].second); } int inDegree[n], outDegree[n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { inDegree[i] = 0 ; outDegree[i] = 0 ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < g[i].size (); j++) { outDegree[i]++; inDegree[g[i][j]]++; } } int rootIndex = -1 , rootCnt = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (inDegree[i] == 0 ) { rootCnt++; rootIndex = i; } } if (rootCnt != 1 ) { return false ; } bool st[n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { st[i] = false ; } dfs (g, rootIndex, st); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (!st[i]) { return false ; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (outDegree[i] > 2 ) { return false ; } if (i == rootIndex) { continue ; } if (inDegree[i] != 1 ) { return false ; } } return true ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 public class Solution { public boolean isBinaryTree (int n, List<Integer[]> edges) { List<List<Integer>> g = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { g.add(new ArrayList <>()); } for (Integer[] e : edges) { g.get(e[0 ]).add(e[1 ]); } int [] inDegree = new int [n]; int [] outDegree = new int [n]; Arrays.fill(inDegree, 0 ); Arrays.fill(outDegree, 0 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j : g.get(i)) { outDegree[i]++; inDegree[j]++; } } int rootIndex = -1 , rootCnt = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (inDegree[i] == 0 ) { rootCnt++; rootIndex = i; } } if (rootCnt != 1 ) { return false ; } boolean [] st = new boolean [n]; dfs(g, rootIndex, st); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (!st[i]) { return false ; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (outDegree[i] > 2 ) { return false ; } if (i == rootIndex) { continue ; } if (inDegree[i] != 1 ) { return false ; } } return true ; } private void dfs (List<List<Integer>> g, int t, boolean [] st) { st[t] = true ; for (int j : g.get(t)) { if (!st[j]) { dfs(g, j, st); } } } }
4 图
4.1 图的存储
这种方式,对于很多算法都很方便,难点在于给定一个图结构,首先需要把给定的图结构转换成该图结构。对于某些算法用不到某些数据,如
入度in和出度out可以不写
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 public class Graph { public HashMap<Integer, Node> nodes; public HashSet<Edge> edges; public Graph () { nodes = new HashMap <>(); edges = new HashSet <>(); } } public class Node { public int value; public int in; public int out; public ArrayList<Node> nexts; public ArrayList<Edge> edges; public Node (int value) { this .value = value; in = 0 ; out = 0 ; nexts = new ArrayList <>(); edges = new ArrayList <>(); } } public class Edge { public int weight; public Node from; public Node to; public Edge (int weight, Node from, Node to) { this .weight = weight; this .from = from; this .to = to; } } public static Graph createGraph (int [][] matrix) { Graph graph = new Graph (); for (int i = 0 ; i < matrix.length; i++) { int weight = matrix[i][0 ]; int from = matrix[i][1 ]; int to = matrix[i][2 ]; graph.nodes.putIfAbsent(from, new Node (from)); graph.nodes.putIfAbsent(to, new Node (to)); Node fromNode = graph.nodes.get(from); Node toNode = graph.nodes.get(to); Edge edge = new Edge (weight, fromNode, toNode); fromNode.nextNodes.add(toNode); fromNode.edges.add(edge); fromNode.out++; toNode.in++; graph.edges.add(edge); edge = new Edge (weight, toNode, fromNode); toNode.nextNodes.add(fromNode); toNode.edges.add(edge); toNode.out++; fromNode.in++; graph.edges.add(edge); } return graph; }
这个版本代码量少,易于理解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Node { public List<Edge> edges = new ArrayList <>(); } class Edge { int n, w; public Edge (int node, int weight) { n = node; w = weight; } } public Node[] createGraph(int [][] matrix, int n) { Node[] graph = new Node [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { graph[i] = new Node (); } for (int i = 0 ; i < matrix.length; i++) { int weight = matrix[i][0 ], from = matrix[i][1 ], to = matrix[i][2 ]; graph[from].edges.add(new Edge (to, weight)); } return graph; }
c++版本
1 2 3 4 5 struct Edge { int n, w; };vector<vector<Edge>> g (n);
4.2 宽度优先遍历
如下所示的图:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public static void bfs (Graph graph) { Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList <>(); Set<Node> visited = new HashSet <>(); visited.add(graph.nodes.get(0 )); queue.add(graph.nodes.get(0 )); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Node node = queue.remove(); System.out.println(node.value); for (Node nextNode : node.nextNodes) { if (!visited.contains(nextNode)) { visited.add(nextNode); queue.add(nextNode); } } } }
4.3 深度优先遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public static void dfs (Graph graph) { Node node = graph.nodes.get(0 ); Set<Node> visited = new HashSet <>(); visited.add(node); recur(node, visited); } public static void recur (Node node, Set<Node> visited) { System.out.println(node.value); for (Node nextNode : node.nextNodes) { if (!visited.contains(nextNode)) { visited.add(nextNode); recur(nextNode, visited); } } }
4.4 拓扑排序
课表排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class Solution { public boolean canFinish (int numCourses, int [][] prerequisites) { Node[] g = new Node [numCourses]; for (int i = 0 ; i < numCourses; i++) { g[i] = new Node (); } int [] in = new int [numCourses]; for (int [] prereq : prerequisites) { g[prereq[1 ]].edges.add(prereq[0 ]); in[prereq[0 ]]++; } int cnt = 0 ; Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < in.length; i++) { if (in[i] == 0 ) { queue.add(i); cnt++; } } while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int node = queue.remove(); for (int n : g[node].edges) { in[n]--; if (in[n] == 0 ) { queue.add(n); cnt++; } } } return cnt == numCourses; } } class Node { List<Integer> edges = new ArrayList <>(); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public static List<Node> sortedTopology (Graph graph) { HashMap<Node, Integer> inMap = new HashMap <>(); Queue<Node> zeroInQueue = new LinkedList <>(); for (Node node : graph.nodes.values()) { inMap.put(node, node.in); if (node.in == 0 ) { zeroInQueue.add(node); } } List<Node> result = new ArrayList <>(); while (!zeroInQueue.isEmpty()) { Node cur = zeroInQueue.poll(); result.add(cur); for (Node next : cur.nexts) { inMap.put(next, inMap.get(next) - 1 ); if (inMap.get(next) == 0 ) { zeroInQueue.add(next); } } } return result; }
4.5 Kruskal算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public static HashMap<Integer, Integer> parent = new HashMap <>();public static int find (int x) { if (parent.get(x) != x) { parent.put(x, find(parent.get(x))); } return parent.get(x); } public static void kruskal (Graph graph) { for (Node node : graph.nodes.values()) { parent.put(node.value, node.value); } Queue<Edge> queue = new PriorityQueue <>((o1, o2) -> o1.weight - o2.weight); queue.addAll(graph.edges); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Edge edge = queue.remove(); int from = find(edge.from.value); int to = find(edge.to.value); if (from != to) { parent.put(from, to); System.out.println(edge.from.value + " " + edge.to.value + " " + edge.weight); } } }
4.6 Prim算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public static void prim (Graph graph) { Queue<Edge> queue = new PriorityQueue <>(); Set<Node> visited = new HashSet <>(); for (Node node : graph.nodes.values()) { if (visited.contains(node)) { continue ; } visited.add(node); queue.addAll(node.edges); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Edge edge = queue.remove(); Node to = edge.to; if (visited.contains(to)) { continue ; } visited.add(to); System.out.println(edge.from.value + " " + edge.to.value + " " + edge.weight); queue.addAll(to.edges); } } }
4.7 前缀Trie树
trie前缀树
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 class Trie { boolean isEnd = false ; Trie[] next = new Trie [26 ]; public Trie () { } public void insert (String word) { if (search(word)) { return ; } char [] words = word.toCharArray(); Trie cur = this ; for (char ch : words) { int index = ch - 'a' ; if (cur.next[index] == null ) { cur.next[index] = new Trie (); } cur = cur.next[index]; } cur.isEnd = true ; } public boolean search (String word) { Trie cur = this ; char [] words = word.toCharArray(); for (char ch : words) { int index = ch - 'a' ; if (cur.next[index] == null ) { return false ; } cur = cur.next[index]; } return cur.isEnd; } public boolean startsWith (String prefix) { Trie cur = this ; char [] words = prefix.toCharArray(); for (char ch : words) { int index = ch - 'a' ; if (cur.next[index] == null ) { return false ; } cur = cur.next[index]; } return true ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 class Trie {public : vector<Trie*> next; bool is_end; Trie () : next (26 ), is_end (false ) {} ~Trie () { for (auto &p : next) { if (p != nullptr ) { delete p; } } } void insert (string word) if (search (word)) { return ; } Trie *cur = this ; for (auto &ch : word) { int index = ch - 'a' ; if (cur->next[index] == nullptr ) { cur->next[index] = new Trie (); } cur = cur->next[index]; } cur->is_end = true ; } bool search (string word) Trie *cur = this ; for (auto &ch : word) { int index = ch - 'a' ; if (cur->next[index] == nullptr ) { return false ; } cur = cur->next[index]; } return cur->is_end; } bool startsWith (string prefix) Trie *cur = this ; for (auto &ch : prefix) { int index = ch - 'a' ; if (cur->next[index] == nullptr ) { return false ; } cur = cur->next[index]; } return true ; } };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 public class Code01_Trie { class Trie { class Node { public int pass; public int end; public Node[] nexts; public Node () { pass = 0 ; end = 0 ; nexts = new Node [26 ]; } } private Node root; public Trie () { root = new Node (); } public void insert (String word) { if (word == null ) { return ; } char [] str = word.toCharArray(); Node node = root; node.pass++; int path = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < str.length; i++) { path = str[i] - 'a' ; if (node.nexts[path] == null ) { node.nexts[path] = new Node (); } node = node.nexts[path]; node.pass++; } node.end++; } public void erase (String word) { if (countWordsEqualTo(word) != 0 ) { char [] chs = word.toCharArray(); Node node = root; node.pass--; int path = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < chs.length; i++) { path = chs[i] - 'a' ; if (--node.nexts[path].pass == 0 ) { node.nexts[path] = null ; return ; } node = node.nexts[path]; } node.end--; } } public int countWordsEqualTo (String word) { if (word == null ) { return 0 ; } char [] chs = word.toCharArray(); Node node = root; int index = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < chs.length; i++) { index = chs[i] - 'a' ; if (node.nexts[index] == null ) { return 0 ; } node = node.nexts[index]; } return node.end; } public int countWordsStartingWith (String pre) { if (pre == null ) { return 0 ; } char [] chs = pre.toCharArray(); Node node = root; int index = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < chs.length; i++) { index = chs[i] - 'a' ; if (node.nexts[index] == null ) { return 0 ; } node = node.nexts[index]; } return node.pass; } } }
4.8 迪杰斯特拉算法
网络延迟时间
普通算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public static Map<Node, Integer> dijkstra (Graph graph) { Map<Node, Integer> distanceMap = new HashMap <>(); Node minNode = graph.nodes.get(0 ); distanceMap.put(minNode, 0 ); Set<Node> visited = new HashSet <>(); while (minNode != null ) { Integer distance = distanceMap.get(minNode); for (Edge edge : minNode.edges) { if (!distanceMap.containsKey(edge.to)) { distanceMap.put(edge.to, distance + edge.weight); } else { distanceMap.put(edge.to, Math.min(distance + edge.weight, distanceMap.get(edge.to))); } } visited.add(minNode); minNode = null ; int minDist = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (Map.Entry<Node, Integer> entry : distanceMap.entrySet()) { Node node = entry.getKey(); Integer dist = entry.getValue(); if (!visited.contains(node) && minDist > dist) { minDist = dist; minNode = node; } } } return distanceMap; }
另一种方式(推荐),图存储方式简单些
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class Solution { public int networkDelayTime (int [][] times, int n, int k) { Node[] g = new Node [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { g[i] = new Node (); } for (int [] time : times) { g[time[0 ] - 1 ].edges.add(new Edge (time[1 ] - 1 , time[2 ])); } int [] dist = new int [n]; Arrays.fill(dist, 0x3f3f3f3f ); boolean [] st = new boolean [n]; dist[k - 1 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i++) { int t = -1 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) { t = j; } } st[t] = true ; for (Edge edge : g[t].edges) { dist[edge.n] = Math.min(dist[edge.n], dist[t] + edge.w); } } int maxDist = Arrays.stream(dist).max().getAsInt(); return maxDist == 0x3f3f3f3f ? -1 : maxDist; } } class Edge { int n, w; public Edge (int node, int weight) { n = node; w = weight; } } class Node { List<Edge> edges = new ArrayList <>(); }
another cpp版本
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class Solution {public : struct Edge { int n, w; }; int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f ; int networkDelayTime (vector<vector<int >>& times, int n, int k) vector<Edge> g[n]; for (auto &time : times) { g[time[0 ] - 1 ].push_back ({time[1 ] - 1 , time[2 ]}); } int dist[n]; bool st[n]; memset (dist, 0x3f , sizeof dist); memset (st, 0 , sizeof st); dist[k - 1 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i++) { int t = -1 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) { t = j; } } st[t] = true ; for (auto &edge : g[t]) { dist[edge.n] = min (dist[edge.n], dist[t] + edge.w); } } int maxDist = *max_element (dist, dist + n); return maxDist == INF ? -1 : maxDist; } };
优化算法
5 贪心算法
5.1 会议安排
LeetCode
646
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int findLongestChain (int [][] pairs) { Arrays.sort(pairs, (a, b) -> a[1 ] - b[1 ]); int retLength = 0 , curTime = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int [] pair : pairs) { if (curTime < pair[0 ]) { retLength++; curTime = pair[1 ]; } } return retLength; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Program { int start, end; } public static int maxMeetings (Program[] programs) { Arrays.sort(programs, (p1, p2) -> p1.end - p2.end); int timePoint = programs[0 ].start; int ret = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < programs.length; i++) { if (timePoint <= programs[i].start) { timePoint = programs[i].end; ret++; } } return ret; }
5.2 字符串数组排序
1 2 3 4 public static void sortString (String[] strs) { Arrays.sort(strs, (s1, s2) -> (s1 + s2).compareTo(s2 + s1)); }
5.3 金条划分
按照上图中的两个不同分割法:
第一种:先划分为10和50,消耗60,再划分为20和30,消耗50,总计110。
第二种:先划分为30和30,消耗60,再划分为10和20,消耗30,总计90。
如果要取到最小的,需要先按照最大的划分,逆向过来,这是一颗哈夫曼树。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public static int lessMoney (int [] arr) { Queue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue <>(); for (int a : arr) { heap.add(a); } int cur = 0 , sum = 0 ; while (heap.size() > 1 ) { cur = heap.remove() + heap.remove(); sum += cur; heap.add(cur); } return sum; }
5.4 利润最大
LeetCode
502
先按照成本花费升序排序,每一轮选出可以做的(成本不大于当前资金的)项目,加入到另一个集合中保存,选出利润最大的做,然后更新当前可用资金。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public int findMaximizedCapital (int k, int w, int [] profits, int [] capital) { Queue<Pair> capHeap = new PriorityQueue <>((p1, p2) -> p1.c - p2.c); Queue<Pair> proHeap = new PriorityQueue <>((p1, p2) -> p2.p - p1.p); for (int i = 0 ; i < profits.length; i++) { capHeap.add(new Pair (profits[i], capital[i])); } for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) { while (!capHeap.isEmpty() && capHeap.peek().c <= w) { proHeap.add(capHeap.remove()); } if (proHeap.isEmpty()) { return w; } w += proHeap.remove().p; } return w; } } class Pair { int p, c; public Pair (int p, int c) { this .p = p; this .c = c; } }
5.5 数据流的中位数(堆的应用)
LeetCode
295
用两个堆,一个大根堆一个小根堆,其中大根堆保存小于等于中位数部分的数据,小根堆保存大于中位数部分的数据。
插入数据算法流程:
如果大根堆空,直接加入大根堆,结束,否则执行2
如果小于等于大根堆堆顶,加入大根堆,否则加入小根堆
判断大小根堆数据量差值,如果插值大于1,则将数据量多的堆的堆顶弹出加入到另一个堆中
查询算法流程:
如果两个堆数据量相同,则大小根堆查询堆顶相加除以2,得到中位数,结束,否则执行2
返回数据量大的堆的堆顶元素
5.5-1.drawio.svg
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 class MedianFinder { private Queue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue <>((a, b) -> b - a); private Queue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue <>(); public MedianFinder () { } public void addNum (int num) { if (maxHeap.isEmpty()) { maxHeap.add(num); return ; } if (num <= maxHeap.peek()) { maxHeap.add(num); } else { minHeap.add(num); } if (maxHeap.size() - minHeap.size() > 1 ) { minHeap.add(maxHeap.remove()); } else if (minHeap.size() - maxHeap.size() > 1 ) { maxHeap.add(minHeap.remove()); } } public double findMedian () { if (maxHeap.size() == minHeap.size()) { return (maxHeap.peek() + minHeap.peek()) / 2.0 ; } if (maxHeap.size() > minHeap.size()) { return maxHeap.peek(); } else { return minHeap.peek(); } } }
6 暴力递归
LeetCode
940
6.1 字符串全排列
LeetCode
46
不去重
去重
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public static List<String> permutation3 (String s) { List<String> ans = new ArrayList <>(); if (s == null || s.length() == 0 ) { return ans; } char [] str = s.toCharArray(); g2(str, 0 , ans); return ans; } public static void g2 (char [] str, int index, List<String> ans) { if (index == str.length) { ans.add(String.valueOf(str)); } else { boolean [] visited = new boolean [256 ]; for (int i = index; i < str.length; i++) { if (!visited[str[i]]) { visited[str[i]] = true ; swap(str, index, i); g2(str, index + 1 , ans); swap(str, index, i); } } } }
6.2 预测赢家
LeetCode
486
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public boolean predictTheWinner (int [] nums) { return dfs(nums, 0 , nums.length - 1 ) >= 0 ; } private int dfs (int [] nums, int i, int j) { if (i == j) { return nums[i]; } int left = nums[i] - dfs(nums, i + 1 , j); int right = nums[j] - dfs(nums, i, j - 1 ); return Math.max(left, right); } }
可以设置两个函数,分别为先手和后手函数。记为f(arr, l, r)和s(arr, l, r)分别表示在arr中的l和r范围内进行决策得到的结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 int f (arr, l, r) { if (l == r) { return arr[l]; } return max(arr[l] + s(arr, l + 1 , r), arr[r] + s(arr, l, r - 1 )); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 int s (arr, l, r) { if (l == r) { return 0 ; } return min(f(arr, l + 1 , r), f(arr, l, r - 1 )); }
1423.
可获得的最大点数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
6.3 解码方法
LeetCode
91
递归方法(会超时)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public int numDecodings (String s) { return numDecodings(s.toCharArray(), 0 ); } public int numDecodings (char [] chs, int i) { if (i == chs.length) { return 1 ; } if (chs[i] == '0' ) { return 0 ; } int ret = numDecodings(chs, i + 1 ); if (chs[i] == '1' ) { if (i + 1 < chs.length) { ret += numDecodings(chs, i + 2 ); } } if (chs[i] == '2' ) { if (i + 1 < chs.length && chs[i + 1 ] < '7' ) { ret += numDecodings(chs, i + 2 ); } } return ret; } }
6.4 n皇后问题
常规方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public static int process1 (int i, int [] record, int n) { if (i == n) { return 1 ; } int res = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (isValid(record, i, j)) { record[i] = j; res += process1(i + 1 , record, n); } } return res; } public static boolean isValid (int [] record, int i, int j) { for (int k = 0 ; k < i; k++) { if (j == record[k] || Math.abs(record[k] - j) == Math.abs(i - k)) { return false ; } } return true ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public static int num2 (int n) { if (n < 1 || n > 32 ) { return 0 ; } int limit = n == 32 ? -1 : (1 << n) - 1 ; return process2(limit, 0 , 0 , 0 ); } public static int process2 (int limit, int colLim, int leftDiaLim, int rightDiaLim) { if (colLim == limit) { return 1 ; } int pos = limit & (~(colLim | leftDiaLim | rightDiaLim)); int mostRightOne = 0 ; int res = 0 ; while (pos != 0 ) { mostRightOne = pos & (~pos + 1 ); pos = pos - mostRightOne; res += process2(limit, colLim | mostRightOne, (leftDiaLim | mostRightOne) << 1 , (rightDiaLim | mostRightOne) >>> 1 ); } return res; }
打印所有可能的n皇后解法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 import java.util.*;class Main { public static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); public static char [][] g; public static int [] record; public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); int n = sc.nextInt(); g = new char [n][n]; record = new int [n]; Arrays.fill(record, -1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { Arrays.fill(g[i], '.' ); } recur(0 , n); sc.close(); } public static void recur (int i, int n) { if (i == n) { sb.setLength(0 ); for (int k = 0 ; k < n; k++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { sb.append(g[k][j]); } sb.append('\n' ); } System.out.println(sb); } else { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (isValid(i, j)) { record[i] = j; g[i][j] = 'Q' ; recur(i + 1 , n); g[i][j] = '.' ; record[i] = -1 ; } } } } public static boolean isValid (int i, int j) { for (int k = 0 ; k < i; k++) { if (j == record[k] || Math.abs(i - k) == Math.abs(j - record[k])) { return false ; } } return true ; } }
51. N 皇后 -
力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 class Solution { public List<List<String>> solveNQueens (int n) { List<List<String>> ret = new ArrayList <>(); char [][] g = new char [n][n]; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); int [] record = new int [n]; Arrays.fill(record, -1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { Arrays.fill(g[i], '.' ); } dfs(0 , n, g, record, ret); return ret; } public void dfs (int i, int n, char [][] g, int [] record, List<List<String>> ret) { if (i == n) { List<String> temp = new ArrayList <>(); for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { temp.add(String.valueOf(g[j])); } ret.add(temp); return ; } for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (isValid(i, j, record)) { record[i] = j; g[i][j] = 'Q' ; dfs(i + 1 , n, g, record, ret); g[i][j] = '.' ; record[i] = -1 ; } } } public boolean isValid (int i, int j, int [] record) { for (int k = 0 ; k < i; k++) { if (j == record[k] || Math.abs(i - k) == Math.abs(j - record[k])) { return false ; } } return true ; } }
7 哈希函数与哈希表
哈希函数的性质(简要记录):
无穷多的值映射到有范围的值
相同的输入得到相同的输出
不同的输入可能得到相同的输出
映射后的值分布比较均匀
7.1 例题
题目:如果有一个40亿条记录的大文件,现需要求出现次数最多的记录,限制内存使用为1GB。摩尔投票法 需要保证重复的记录超过总记录数的一半。
7.2 布隆过滤器
主要用于类似黑名单系统 ,查找当前记录是否存在于“黑名单”中,并且这个黑名单只会添加记录,不会删除记录,使用布隆过滤器可以比使用hash表大大减少空间。但是布隆过滤器存在一定的失误率,即不存在于黑名单的记录可能也会认为是黑名单,可以通过设置大小大大降低失误率,但是失误率是一直存在的。算法过程:
准备
添加黑名单
遍历黑名单记录列表
遍历哈希函数
每个哈希函数求得一个哈希值
将位集合中的
判断是否在黑名单中
对于一个记录遍历哈希函数
求得一个哈希值
判断是否为1
当所有的位置都为1时说明在黑名单中(可能存在失误),否则不在
首先需要构造一个二进制位集合,这里可以采用int数组的形式,每一个值表示32位
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 int a[ceil (m / 32 )];void setI1 (int *a, int i) int index = i / 32 , bit_index = i % 32 ; a[index] = a[index] | (1 << bit_index); } void setI0 (int *a, int i) int index = i / 32 , bit_index = i % 32 ; a[index] = a[index] & (~(1 << bit_index)) } int getI (int *a, int i) { int index = i / 32 , bit_index = i % 32 ; return (a[index] >> bit_index) & 1 ; }
🍰真 真 真 真 真 真
7.3 一致性哈希
服务器利用hash
key进行划分做负载均衡,尽量选取种类多,且分布较均匀的key。否则会导致某些服务器资源利用过多(如某些key使用很多,但另一些使用很少)。如果后期需要增加服务器或者减少,则会导致数据迁移,而这个数据迁移是全量的迁移。
无法保证初始分配的节点比较少时是均匀分配的(hash计算能保证大数据量的情况下是均分的)
添加一个节点后也不能保证添加之后是均分的
8 有序表、并查集
岛屿问题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 int getIsland (vector<vector<int >> &m, int N, int M) int ret = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < N; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < M; j++) { if (m[i][j] == 1 ) { ret++; dfs (m, i, j, N, M); } } } return ret; } void dfs (vector<vector<int >> &m, int i, int j, int N, int M) if (i < 0 || i >= N || j < 0 || j >= M || m[i][j] == 0 ) { return ; } m[i][j] = 2 ; dfs (m, i - 1 , j, N, M); dfs (m, i, j - 1 , N, M); dfs (m, i + 1 , j, N, M); dfs (m, i, j + 1 , N, M); }
时间复杂度左神视频链接
8.1 并查集
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class UnionFind { private int [] p; public UnionFind (int n) { p = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { p[i] = i; } } public int find (int x) { if (x != p[x]) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } public void union (int a, int b) { int pa = find(a); int pb = find(b); if (pa != pb) { p[pa] = pb; } } }
9 KMP算法