盛最多水的容器
https://leetcode.cn/problems/container-with-most-water/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked for循环会导致超时。
计算体积,比较大小
比较左右指针所在位置的高度
高度低的向内收缩
🍰 证明:i, j所在位置的高度为x, y,用S(i, j)表示指针位置形成的体积大小。这里假设x < y。如果按照上述收缩思路的话,应该是i向右移,形成的体积大小是S(i + 1, j)。这里会有疑问的是丢失了S(i, j - 1), S(i, j - 2), ..., S(i, i + 1)的状态。下面证明这些状态都小于S(i, j)。j - i的长度为w,然后丢失状态的所有容器的长度(j - t) - i设为w'都一定小于w。i指针不动,高度为x,右指针向内收缩,高度设为y',可以知道y'和y的大小关系不确定。分为两种情况:
y' > y,那么S(i, j - t)的体积为w' * x,一定小于S(i, j) = w * x。y' <= y,那么S(i, j - t)的体积为min(x, y') * w'
x > y',S(i, j - t) = y' * w'一定小于w * xx <= y',S(i, j - t) = x * w'一定小于w * x
所以如果移动高位置的指针,一定会导致容器体积减小,移动低位置的可能会使得容器体积增大。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int maxArea (int [] height) { int result = 0 ; for (int i = 0 , j = height.length - 1 ; i < j;) { result = Math.max(result, Math.min(height[i], height[j]) * (j - i)); if (height[i] < height[j]) { i++; } else { j--; } } return result; } }
三数之和
https://leetcode.cn/problems/3sum/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked for循环会超时。k,取另外两个指针i j分别在k + 1, nums.length - 1的位置,然后判断:
nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[j] > 0则整体偏大,需要减小,可以让j--nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[j] < 0则整体偏小,需要增大,可以让i++否则满足条件,加入结果列表
这里需要注意要排除重复的三元组,因此在移动指针时需要判断后续判断的值是否和当前值冲突
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> threeSum (int [] nums) { Arrays.sort(nums); List<List<Integer>> resultList = new ArrayList <>(); for (int k = 0 ; k < nums.length; k++) { if (k > 0 && nums[k] == nums[k - 1 ]) { continue ; } if (nums[k] > 0 ) { return resultList; } for (int i = k + 1 , j = nums.length - 1 ; i < j;) { int temp = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k]; if (temp > 0 ) { while (i < j && nums[j] == nums[--j]); } else if (temp < 0 ) { while (i < j && nums[i] == nums[++i]); } else { resultList.add(Arrays.asList(nums[k], nums[i], nums[j])); while (i < j && nums[i] == nums[++i]); while (i < j && nums[j] == nums[--j]); } } } return resultList; } }
最长连续序列
https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-consecutive-sequence/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked O(n),如果直接排序的话复杂度达到O(nlogn)。nums[i],然后将这个数一直+1,加完后的数在数组里还能找到那就说明连续序列的长度可以增加
1。因此满足这个条件的话需要使用到哈希,将所有的数保存在一个集合中,方便查询。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public int longestConsecutive (int [] nums) { Set<Integer> numSet = new HashSet <>(); for (int num : nums) { numSet.add(num); } int result = 0 ; for (int num : nums) { if (numSet.contains(num - 1 )) { continue ; } int tempResult = 1 ; int temp = num; while (numSet.contains(++temp)) { tempResult++; } result = Math.max(result, tempResult); } return result; } }
接雨水
https://leetcode.cn/problems/trapping-rain-water/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked 按列求 ,单独考虑每个柱子可以接到的雨水。左侧和右侧 的最高的柱子包裹起来,可以保证接到雨水,而接到的雨水的多少则是右两则最高的柱子中的矮 的决定(木桶效应)。如果矮的柱子比当前柱子高,那么接到的雨水就是高度的差值,否则接不到雨水。当前柱子左侧最高的高度 和当前柱子右侧最高的高度 。
动态规划
使用一个数组 记录当前位置左侧(不包括自身)最高的高度是多少,即maxLeft[i] = max(maxLeft[i - 1], height[i - 1]),右侧同理O(n)的空间复杂度
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int trap (int [] height) { int [] maxLeft = new int [height.length]; int [] maxRight = new int [height.length]; for (int i = 1 ; i < height.length; i++) { maxLeft[i] = Math.max(maxLeft[i - 1 ], height[i - 1 ]); } for (int i = height.length - 2 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { maxRight[i] = Math.max(maxRight[i + 1 ], height[i + 1 ]); } int sum = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < height.length - 1 ; i++) { int min = Math.min(maxLeft[i], maxRight[i]); int sub = min - height[i]; sum += sub > 0 ? sub : 0 ; } return sum; } }
无重复字符的最长子串
https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked j, i为滑动窗口的边界,表示[j, i]区间的字符串都不重复。并且使用一个Set集合保存该窗口中的字符,遍历时如果待加入的字符已经存在了,则一直遍历删除窗口左端的字符直到没有重复的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) { char [] chs = s.toCharArray(); Set<Character> set = new HashSet <>(); int result = 0 ; for (int i = 0 , j = 0 ; i < chs.length; i++) { while (set.contains(chs[i])) { set.remove(chs[j++]); } set.add(chs[i]); result = Math.max(result, set.size()); } return result; } }
和为 K 的子数组
https://leetcode.cn/problems/subarray-sum-equals-k/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked 区间内数值的和 ,这样可以想到使用前缀和 来计算,前缀和数组preSum[i]表示原数组nums中第一个数一直加到第i个数的和,如果表示某一段区间[j, i]的和,计算preSum[i] - preSum[j - 1]即可。(0, 1)键值对表示前缀和为 0
的有一个(前缀和中什么数都没有),暂时还不理解。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public int subarraySum (int [] nums, int k) { int n = nums.length; int [] preSum = new int [n + 1 ]; Arrays.fill(preSum, 0 ); for (int i = 1 ; i < n + 1 ; i++) { preSum[i] = preSum[i - 1 ] + nums[i - 1 ]; } int result = 0 ; Map<Integer, Integer> mp = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < n + 1 ; i++) { if (mp.containsKey(preSum[i] - k)) { result += mp.get(preSum[i] - k); } mp.put(preSum[i], mp.getOrDefault(preSum[i], 0 ) + 1 ); } return result; } }
滑动窗口最大值
https://leetcode.cn/problems/sliding-window-maximum/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked 单调队列 ,但是具体实现采用双端队列 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int [] maxSlidingWindow(int [] nums, int k) { int [] resultArr = new int [nums.length - (k - 1 )]; Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList <>(); for (int i = 0 , j = 1 - k; i < nums.length; i++, j++) { if (j > 0 && deque.getFirst() == nums[j - 1 ]) { deque.removeFirst(); } while (deque.size() != 0 && deque.getLast() < nums[i]) { deque.removeLast(); } deque.addLast(nums[i]); if (j >= 0 ) { resultArr[j] = deque.getFirst(); } } return resultArr; } }
另一种写法,队列中保存的是窗口中元素的下标,通过下标判断元素是否在窗口中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int [] maxSlidingWindow(int [] nums, int k) { int [] resultArr = new int [nums.length - (k - 1 )]; Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList <>(); for (int i = 0 , j = 1 - k; i < nums.length; i++, j++) { if (j > 0 && deque.getFirst() < j) { deque.removeFirst(); } while (deque.size() != 0 && nums[deque.getLast()] < nums[i]) { deque.removeLast(); } deque.addLast(i); if (j >= 0 ) { resultArr[j] = nums[deque.getFirst()]; } } return resultArr; } }
最小覆盖子串
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-window-substring/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked 滑动窗口,窗口由两个指针控制大小,右指针负责扩大窗口,左指针负责收缩窗口。如果当前窗口不覆盖子串,则扩大窗口,如果覆盖子串,则收缩窗口更新结果,直至不能收缩。
❓问题在于如何判断是否覆盖?
可以使用哈希表存储窗口中每个字符出现的次数,如果目标字符串中的字符出现的次数都小于等于 窗口中的,则说明覆盖,否则不覆盖。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution { public String minWindow (String s, String t) { char [] chsArr = s.toCharArray(); char [] chtArr = t.toCharArray(); Map<Character, Integer> chCntMp = new HashMap <>(); for (char ch : chtArr) { chCntMp.put(ch, chCntMp.getOrDefault(ch, 0 ) + 1 ); } Map<Character, Integer> winMap = new HashMap <>(); int ansLeft = -1 , ansRight = chsArr.length; for (int i = 0 , j = 0 ; i < chsArr.length; i++) { winMap.put(chsArr[i], winMap.getOrDefault(chsArr[i], 0 ) + 1 ); while (isCover(winMap, chCntMp)) { if (i - j + 1 < ansRight - ansLeft + 1 ) { ansRight = i; ansLeft = j; } winMap.put(chsArr[j], winMap.get(chsArr[j++]) - 1 ); } } return ansLeft == -1 ? "" : s.substring(ansLeft, ansRight + 1 ); } public boolean isCover (Map<Character, Integer> s, Map<Character, Integer> t) { if (s.size() < t.size()) { return false ; } for (Map.Entry<Character, Integer> entry : t.entrySet()) { if (s.getOrDefault(entry.getKey(), 0 ) < entry.getValue()) { return false ; } } return true ; } }
最大子数组和
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-subarray/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked 动态规划 可以达到O(N)的时间复杂度。dp[i]表示以第 i
个数结尾的最大的子数组的和,所以递归公式:dp[i] = max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i]),如果前一个子数组加上nums[i]数组和变小,就认为最大的数组是nums[i]自己。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) { int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (i > 0 ) { nums[i] = Math.max(nums[i], nums[i - 1 ] + nums[i]); } ans = Math.max(ans, nums[i]); } return ans; } }
轮转数组
https://leetcode.cn/problems/rotate-array/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked O(1),不适用额外的数组。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public void rotate (int [] nums, int k) { k %= nums.length; reverse(nums, 0 , nums.length - 1 ); reverse(nums, 0 , k - 1 ); reverse(nums, k, nums.length - 1 ); } private void reverse (int [] nums, int start, int end) { for (int i = start, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) { int temp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = temp; } } }
缺失的第一个正数
41.
缺失的第一个正数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难点在于不能使用额外空间。如果可以使用额外空间,可以使用哈希表,存储每一个元素,然后从
1 开始遍历,直到发现不存在于哈希表中的值即可。
如果要降低空间复杂度,可以考虑原地哈希 。
通过观察结果,会发现,结果肯定存在于[1, n+1]中,n
为数组长度,如果数组中的数在[1, n]都存在,则说明结果为 n + 1,否则为[1,
n]中不存在的最小的数,这里可以使用原地哈希,具体方法可以采用标记法 ,遍历数组,如果
nums[i]范围在[1, n]中,则给 nums[nums[i] -
1]打上标记,这里打标记可以设置为负数,因为原数组中存在负数,可以令原来的负数设为一个不可能的值,如
n + 1
或者更大,这样所有数都是正数了。当遍历完所有打完标记,如果所有的数都是负数了,说明都存在了,否则为第一个不为负数的下标+
1。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int firstMissingPositive (int [] nums) { for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] <= 0 ) { nums[i] = nums.length + 1 ; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { int temp = Math.abs(nums[i]); if (temp >= 1 && temp <= nums.length) { nums[temp - 1 ] = -Math.abs(nums[temp - 1 ]); } } for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] > 0 ) { return i + 1 ; } } return nums.length + 1 ; } }
旋转图像
48.
旋转图像 - 力扣(LeetCode)
所以接下来的重点是寻找旋转链之间的对应的坐标关系。以左上角的(i, j)为例,
旋转一次后的坐标为:(j, n - i - 1),可以理解为,(i, j)所在的列变成了行,行变成了列。从行看,i行的数据会变成列,行是从上往下数,那么变成列后就是从右往左数,所以列就是n - i - 1。从列看,从左向右看,变成行就是从上往下看,因此就是j。
(j, n - i - 1)再旋转一次后,坐标为:(n - i - 1, n - j - 1),从行看,是从上往下,旋转后的列则是从右向左,所以是n - j - 1。从列看,从右往左,旋转后的行则是从下往上,n - i - 1
依此类推:(n - j - 1, i)
最后的坐标旋转链(i, j) -> (j, n - i - 1) -> (n - i - 1, n - j - 1) -> (n - j - 1, i) -> (i, j)
因此,原地操作只需要按照这个顺序依次赋值即可。
接下来需要考虑的是,遍历哪些数据进行旋转操作。只有两种情况,n
为奇数和偶数的情况。
n 为偶数:只需要考虑左上角 行[0, n / 2)
列[0, n / 2)的情况
n
为奇数:不需要考虑正中心的数,然后需要旋转的则是正中心左方和上方组成的区域,即
行[0, n / 2) 列[0, n / 2]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public void rotate (int [][] matrix) { int n = matrix.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < n / 2 ; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < (n + 1 ) / 2 ; j++) { int temp = matrix[i][j]; matrix[i][j] = matrix[n - 1 - j][i]; matrix[n - 1 - j][i] = matrix[n - 1 - i][n - 1 - j]; matrix[n - 1 - i][n - 1 - j] = matrix[j][n - 1 - i]; matrix[j][n - 1 - i] = temp; } } } }
相交链表
160.
相交链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
判断两个链表是否相交,可以使用双指针的方式,题目中保证链表中不存在环,因此大大简化了判断条件。
两个指针分别遍历两个链表,当遍历到末尾时再遍历另一个链表,直到指向相同的节点,即为相交的第一个节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { return getIntersectionNode(headA, headB, null ); } private ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB, ListNode endNode) { if (headA == null || headB == null ) { return null ; } ListNode pA = headA; ListNode pB = headB; while (pA != pB) { pA = pA == endNode ? headB : pA.next; pB = pB == endNode ? headA : pB.next; } return pA; } }
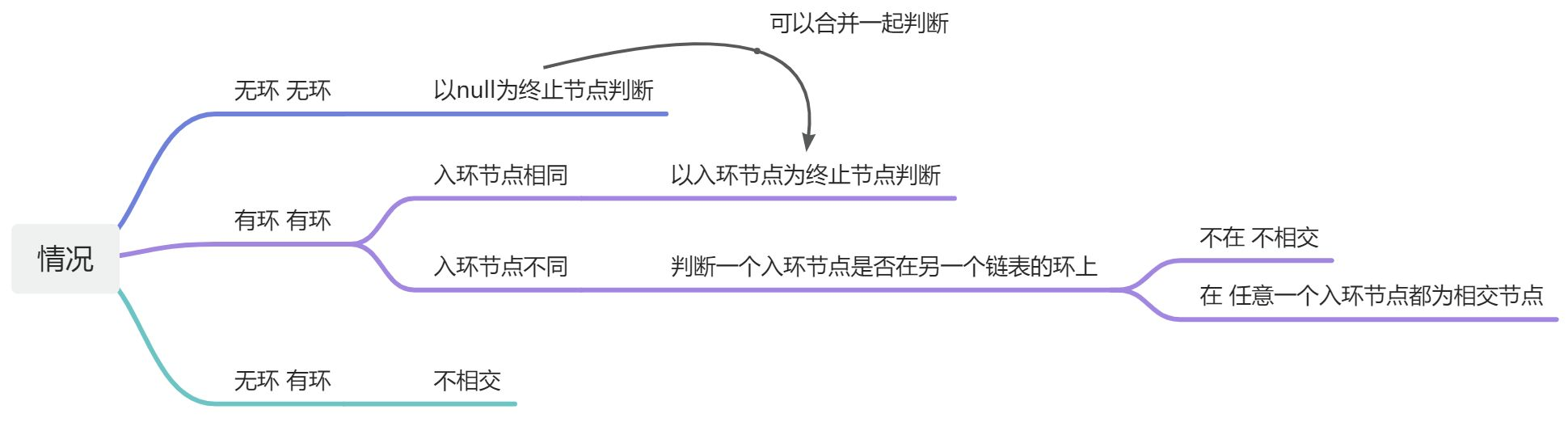
❓ 如果链表中存在环呢?则需要考虑多种情况。
这里认为链表都是单链表
情况 1:两个链表都无环双指针,遍历链表 A 和 B,当指针为 null
时从另一个节点的头节点开始遍历。直到两个指针相等(两个指针相等时,如果为
null 则表示没有相交节点,否则有相交节点)面试题
02.07. 链表相交 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { if (headA == null || headB == null ) { return null ; } ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB; while (pA != pB) { pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next; pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next; } return pA; } }
❗注意 :判断是否为null时,使用的是pA当前指针,而不是pA.next,如果使用pA.next来判断,当不相交时,会发生无限循环的情况,pA和pB会一直不相等(也不为null)。所以使用pA当前指针。可以理解为,把最后链表结束时指向的null指针也算作一个节点,然后两个链表不相交时,最后都会指向null节点,那么两个链表就在null节点“相交”了,如下图所示。
情况
2:一个有环一个无环(一定不相交)如果相交,则肯定有一个节点有两个next指针,这不满足单链表。所以一定不相交。
情况 3:两个都有环
相交只有两种情况
找到两个带环链表的入环节点,然后固定一个,遍历另一个,直到能找到一个节点和固定节点相等,则证明相交,否则不相交。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 if (circleNode1 == circleNode2) { return true ; } Node temp = circleNode2.next;while (temp != circleNode2) { if (temp == circleNode1) return true ; temp = temp.next; } return false ;
所以所有情况如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 public static ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { ListNode cycleNodeA = hasCycle(headA); ListNode cycleNodeB = hasCycle(headB); if (cycleNodeA == cycleNodeB) { return getIntersectionNodeNoLoop(headA, headB, cycleNodeA); } if (cycleNodeA == null || cycleNodeB == null ) { return null ; } ListNode temp = cycleNodeA; while (temp != cycleNodeB) { temp = temp.next; if (temp == cycleNodeA) { return null ; } } return cycleNodeA; } public static ListNode hasCycle (ListNode head) { if (head == null ) { return null ; } ListNode slow = head, fast = head; while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null ) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (fast == slow) { fast = head; while (fast != slow) { fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } return fast; } } return null ; } public static ListNode getIntersectionNodeNoLoop (ListNode headA, ListNode headB, ListNode endNode) { ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB; while (pA != pB) { pA = pA == endNode ? headB : pA.next; pB = pB == endNode ? headA : pB.next; } return pA; }
反转链表
206.
反转链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
使用三个指针分别指向“上一个节点”“当前节点”和“下一个节点”,遍历过程中反转“上一个节点”和“当前节点”的指向。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null , cur = head; while (cur != null ) { ListNode next = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = next; } return pre; } }
回文链表
234.
回文链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
需要使用O(1)的空间复杂度,回文的定义:从前向后和从后向前遍历的结果相同。但是原链表是单向链表,因此如果想从后向前遍历,需要将后半部分的链表反转。
因此需要判断什么时候到达了“中间”位置,然后将中间及其之后的链表反转。
这里使用快慢指针,因为快指针行进速度是慢指针 2
倍,所以当快指针到结尾时,慢指针行进了链表长度的一半。
这里分两种情况考虑,链表长度为奇数和偶数。
如图所示,当快慢指针结束时,奇数长度的链表慢指针在正中心的位置,偶数长度的链表慢指针在前半部分的最后一个节点位置。
通过观察可以知道,奇数长度的链表正中心的节点并不影响整体的回文性,偶数长度的链表需要将后半部分的链表反转,因此可以确定需要反转的链表的头节点 为slow.next,反转完后返回右半部分头节点,从左半部分头节点和右半部分头节点同时遍历,如果不同则直接返回false,需要注意终止条件是右半部分的节点走到null,因为链表长度为奇数时,左半部分的链表会多一个中心节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 class Solution { public boolean isPalindrome (ListNode head) { if (head == null ) { return true ; } ListNode fast = head, slow = head; while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null ) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; } fast = reverse(slow.next); ListNode temp = fast; slow = head; while (fast != null ) { if (fast.val != slow.val) { return false ; } fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } reverse(temp); return true ; } private ListNode reverse (ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null , cur = head; while (cur != null ) { ListNode next = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = next; } return pre; } }
环形链表
142.
环形链表 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
判断链表是否有环,使用快慢指针,当快慢指针相遇时表明存在环,然后将快指针从头节点开始遍历,每次移动一个位置,直到再次相遇的节点即为环形的入口。
❓ 为什么将快指针从头节点开始遍历就能找到入口?下边给出证明:
假设环形链表中三个点,头节点 A,入口节点 B,快慢指针相遇的节点
C。因为快指针的速度是慢指针的 2 倍,所以快指针行进的距离是慢指针的 2
倍,所以有
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle (ListNode head) { if (head == null ) { return null ; } ListNode slow = head, fast = head; while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null ) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (slow == fast) { fast = head; while (slow != fast) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } return fast; } } return null ; } }
删除链表的倒数第 N 个节点
19.
删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
要求使用一趟遍历,难点在于遍历一趟就要找到第 N
个节点所在的位置。如果只用一个指针遍历长度,则需要遍历两次。
如果使用两个指针,让第一个指针先走n - 1步,然后让第二个指针和第一个指针同时行进,则可以保证两个指针的距离固定,当第一个指针到达结尾时,第二个指针的位置则为需要删除的节点,然后进行删除即可。(注意:需要多一个pre指针,不然无法删除)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public ListNode removeNthFromEnd (ListNode head, int n) { ListNode first = head; ListNode second = head; ListNode pre = null ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i++) { first = first.next; } while (first.next != null ) { first = first.next; pre = second; second = second.next; } if (pre == null ) { return head.next; } pre.next = second.next; return head; } }
两两交换链表中的节点
24.
两两交换链表中的节点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
采用“类似头插法”方式,设置一个temp节点,temp节点指向的后续的节点即为需要交换的节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { public ListNode swapPairs (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null ) { return head; } ListNode ansHead = new ListNode (); ansHead.next = head; ListNode temp = ansHead; while (temp.next != null && temp.next.next != null ) { ListNode node1 = temp.next; ListNode node2 = temp.next.next; temp.next = node2; node1.next = node2.next; node2.next = node1; temp = node1; } return ansHead.next; } }
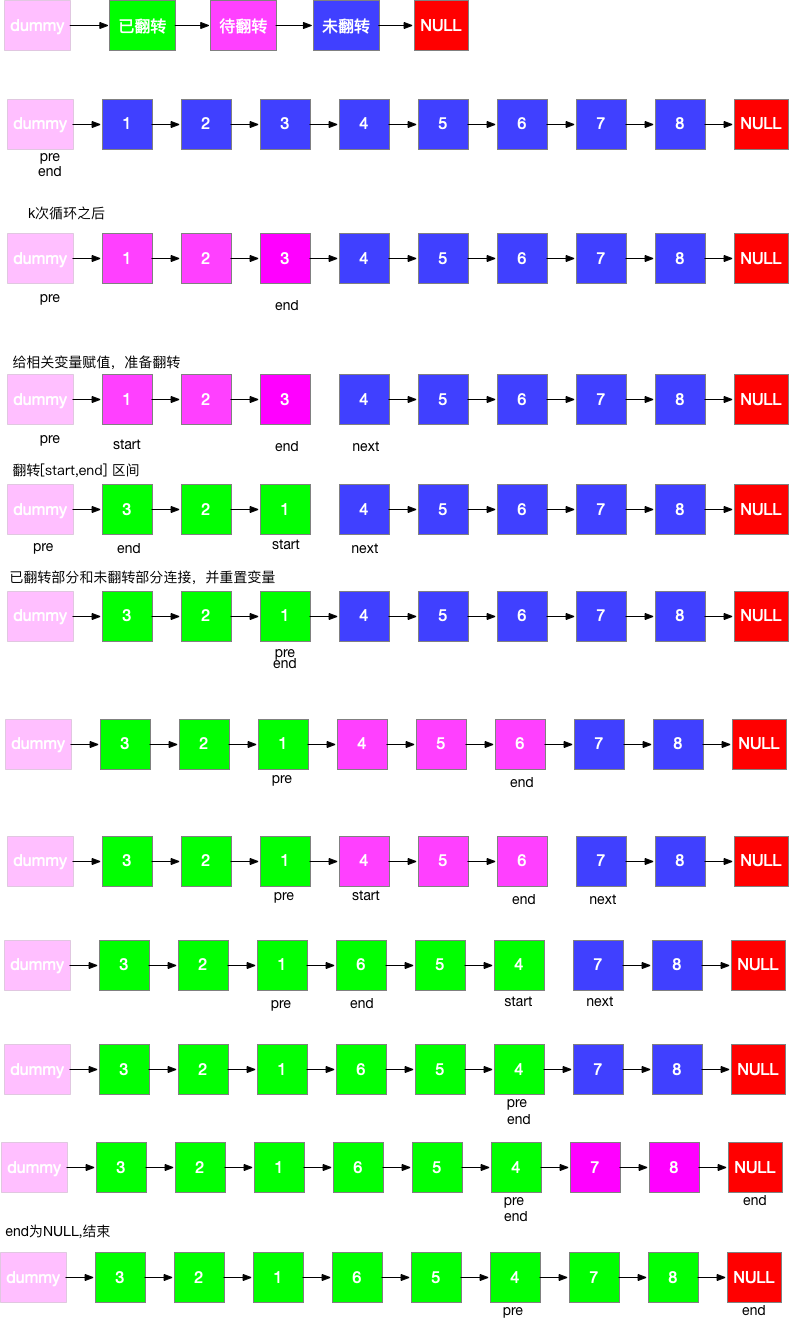
K 个一组翻转链表
25.
K 个一组翻转链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
要求 K 个一组,可以参考删除链表的倒数第 N
个节点 ,先走 K 步,然后翻转这 K 个链表,依此类推。
需要注意的是设置一个dummy节点,即带头节点,方便后续操作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 var reverseKGroup = function (head, k ) { let dummy = new ListNode (0 , head); let pre = dummy, cur = dummy; while (cur.next !== null ) { for (let i = 0 ; i < k && cur; i++) { cur = cur.next ; } if (!cur) { break ; } let start = pre.next , end = cur.next ; pre.next = reverse (start, end); start.next = end; pre = start; cur = start; } return dummy.next ; }; function reverse (head, end ) { if (!head) { return null ; } let pre = null , cur = head; while (cur !== end) { let next = cur.next ; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = next; } return pre; }
随机链表的复制
138.
随机链表的复制 - 力扣(LeetCode)
方法一: 哈希表,存储每个节点的对应复制的节点,然后遍历添加指针。
方法二:
构造新链表旧链表1 -> 新链表1 -> 旧链表2 -> 新链表2 -> ... -> 旧链表n -> 新链表n,然后遍历,通过旧链表的random指针,找到新链表的random节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 var copyRandomList = function (head ) { if (!head) { return null ; } let temp = head; while (temp) { let node = new _Node (temp.val , temp.next , null ); temp.next = node; temp = node.next ; } temp = head; while (temp) { if (temp.random ) { temp.next .random = temp.random .next ; } temp = temp.next .next ; } temp = head; let ansHead = head.next ; let ansTemp = ansHead; while (temp) { temp.next = ansTemp.next ; temp = ansTemp.next ; if (temp) { ansTemp.next = temp.next ; ansTemp = temp.next ; } } return ansHead; };
排序链表
148.
排序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
链表排序,通常使用归并排序。
利用快慢指针找到中点,然后两边分别排序、归并。
注意 的是 ?? 和 || 的区别:
x ?? y是当x为null、undefined时取
y,如果x为false、0、''这种仍然取x。x || y当x为假值 即null、undefined、false、0、''这些值时取y
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 var sortList = function (head ) { if (!head || !head.next ) { return head; } let fast = head, slow = head; while (fast.next && fast.next .next ) { fast = fast.next .next ; slow = slow.next ; } let mid = slow.next ; slow.next = null ; let left = sortList (head); let right = sortList (mid); let ansHead = new ListNode (); let tail = ansHead; while (left && right) { if (left.val < right.val ) { tail.next = left; left = left.next ; } else { tail.next = right; right = right.next ; } tail = tail.next ; } tail.next = left ?? right; return ansHead.next ; };
合并 K 个升序链表
23.
合并 K 个升序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
归并排序的思想,每两个合成一个,然后继续合成,直到剩下最后一个。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 var mergeKLists = function (lists ) { if (lists.length === 0 ) { return null ; } return mergeList (lists, 0 , lists.length - 1 ); }; function mergeList (lists, left, right ) { if (left >= right) { return lists[left]; } let mid = (left + right) >> 1 ; let leftList = mergeList (lists, left, mid); let rightList = mergeList (lists, mid + 1 , right); let dummy = new ListNode (); let tail = dummy; while (leftList && rightList) { if (leftList.val < rightList.val ) { tail.next = leftList; leftList = leftList.next ; } else { tail.next = rightList; rightList = rightList.next ; } tail = tail.next ; } tail.next = leftList ?? rightList; return dummy.next ; }
实现 LRU 缓存
146.
LRU 缓存 - 力扣(LeetCode)
最近最少使用缓存,可以使用一个链表保存数据,如果被使用了则放在链表头或者尾,这样一来,链表的某个方向上就是最近的使用频率递减的趋势。同时使用链表移动数据的操作是
O(1)的。
但是查找很耗时,因此可以采用哈希的方式,存储每个 key
对应的链表的节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 class ListNode { constructor (val, pre, next ) { this .val = val ?? { key : 0 , value : 0 }; this .pre = pre ?? null ; this .next = next ?? null ; } } var LRUCache = function (capacity ) { this .capacity = capacity; this .size = 0 ; this .dummyHead = new ListNode (); this .dummyTail = new ListNode (); this .dummyHead .next = this .dummyTail ; this .dummyTail .pre = this .dummyHead ; this .kv = new Map (); }; LRUCache .prototype get = function (key ) { if (!this .kv .has (key)) { return -1 ; } const temp = this .kv .get (key); removeNode (temp); addToTail (this .dummyTail , temp); return temp.val .value ; }; LRUCache .prototype put = function (key, value ) { if (this .kv .has (key)) { const temp = this .kv .get (key); temp.val .value = value; removeNode (temp); addToTail (this .dummyTail , temp); } else { const temp = new ListNode ({ key, value }); addToTail (this .dummyTail , temp); this .kv .set (key, temp); if (this .size < this .capacity ) { this .size ++; } else { this .kv .delete (this .dummyHead .next .val .key ); removeNode (this .dummyHead .next ); } } }; function removeNode (temp ) { temp.pre .next = temp.next ; temp.next .pre = temp.pre ; } function addToTail (dummyTail, temp ) { temp.next = dummyTail; temp.pre = dummyTail.pre ; dummyTail.pre = temp; temp.pre .next = temp; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 struct Node { int key, val; Node *next; Node *prev; Node (int key, int val) { this ->key = key; this ->val = val; this ->next = nullptr ; this ->prev = nullptr ; } Node (int key, int val, Node *next, Node *prev) { this ->key = key; this ->val = val; this ->next = next; this ->prev = prev; } }; class LRUCache {public : int size; unordered_map<int , Node*> hash; Node *dummyHead; Node *dummyTail; LRUCache (int capacity) { size = capacity; dummyHead = new Node (0 , 0 ); dummyTail = new Node (0 , 0 ); dummyHead->next = dummyTail; dummyTail->prev = dummyHead; } void addNodeToHead (Node *temp) temp->next = dummyHead->next; temp->prev = dummyHead; dummyHead->next->prev = temp; dummyHead->next = temp; } void removeNode (Node *temp) temp->prev->next = temp->next; temp->next->prev = temp->prev; } int get (int key) if (!hash.count (key)) { return -1 ; } auto temp = hash[key]; removeNode (temp); addNodeToHead (temp); return temp->val; } void put (int key, int value) if (hash.count (key)) { auto temp = hash[key]; temp->val = value; removeNode (temp); addNodeToHead (temp); } else { auto temp = new Node (key, value); hash[key] = temp; addNodeToHead (temp); if (hash.size () > size) { auto removed = dummyTail->prev; removeNode (removed); hash.erase (removed->key); delete removed; } } } };
二叉树的层序遍历
102.
二叉树的层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
层序遍历使用队列即可,但是题目中要求每一层的数据单独作为一个子数组保存。
在每次遍历队列之前,可以获取队列的长度,即表示当前层的节点个数。然后一次性遍历当前层所有的节点,下一次遍历的时候,就是遍历的下一层的节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 var levelOrder = function (root ) { if (!root) { return []; } const ans = []; const que = [root]; while (que.length ) { const ret = []; const size = que.length ; for (let i = 0 ; i < size; i++) { const temp = que.shift (); ret.push (temp.val ); if (temp.left ) { que.push (temp.left ); } if (temp.right ) { que.push (temp.right ); } } ans.push (ret); } return ans; };
将有序数组转为平衡二叉搜索树
108.
将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
要求为平衡二叉树,利用二分查找得到的搜索树是平衡的,可以利用二分查找的思路构造。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 var sortedArrayToBST = function (nums ) { return recur (nums, 0 , nums.length - 1 ); }; function recur (nums, left, right ) { if (left === right) { return new TreeNode (nums[left]); } else if (left > right) { return null ; } const mid = (left + right) >> 1 ; const root = new TreeNode (nums[mid]); root.left = recur (nums, left, mid - 1 ); root.right = recur (nums, mid + 1 , right); return root; }
验证是否是二叉搜索树
98.
验证二叉搜索树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
利用二叉搜索树的性质,中序遍历的结果是有序的。因此可以采用中序遍历,同时使用一个变量保存遍历时上次的结果,当前值大于上一次的值 并且左右子树都为二叉搜索树 才为二叉搜索树。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 var isValidBST = function (root ) { let pre = Number .MIN_SAFE_INTEGER ; function recur (root ) { if (!root) { return true ; } const leftBST = recur (root.left ); const cur = root.val ; if (pre < cur) { pre = cur; } else { return false ; } const rightBST = recur (root.right ); return leftBST && rightBST; } return recur (root); };
二叉搜索树第 K 小的元素
230.
二叉搜索树中第 K 小的元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
由二叉搜索树的性质,中序遍历为从小到大的序列,可以采用中序遍历的方式,遍历到第
K 个数的时候记录值,即为第 K 小的元素。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 var kthSmallest = function (root, k ) { let ans = 0 ; function recur (root ) { if (!root) { return ; } recur (root.left ); if (k === 0 ) { return ; } if (k === 1 ) { ans = root.val ; } k--; recur (root.right ); } recur (root); return ans; };
二叉树的右视图
199.
二叉树的右视图 - 力扣(LeetCode)
要求每一层的最右边的数据,可以考虑用层序遍历,每一层的最后一个数据为结果集的数据。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 var rightSideView = function (root ) { if (!root) { return []; } const ans = []; const que = []; que.push (root); while (que.length ) { const size = que.length ; for (let i = 0 ; i < size; i++) { const temp = que.shift (); if (i === size - 1 ) { ans.push (temp.val ); } if (temp.left ) { que.push (temp.left ); } if (temp.right ) { que.push (temp.right ); } } } return ans; };
二叉树展开为链表
114.
二叉树展开为链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
按照先序遍历方式展开,左指针始终为
null,而元素都在右指针,考虑按照递归的做法,将左右子树分别展开,然后将左子树的节点(如果有)链接到右子树上。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 var flatten = function (root ) { if (!root) { return null ; } flatten (root.left ); flatten (root.right ); let temp = root.left ; if (temp) { while (temp.right ) { temp = temp.right ; } temp.right = root.right ; root.right = root.left ; root.left = null ; } };
要求使用O(1)的空间复杂度,不使用前序遍历的方式,转换思路。
前序遍历特点为:根、左、右 ,如果要展开成一个链表,则当前节点curr的右子节点,一定排在curr的左子树的某个节点之后。根据特点,可以知道,左子树的最后一个节点一定是左子树(非空)最右侧的节点,因此找到后,可以认为这个最右侧的节点是当前节点的右子节点的前驱结点prev,将prev的右孩子设置为当前节点的右子节点,将当前节点的左子树设置为右孩子(因为左子树一定是当前节点的后驱节点),并将左子树置空。将当前节点向右孩子走一步,完成一轮循环。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution {public : void flatten (TreeNode* root) if (!root) return ; auto curr = root; while (curr) { if (curr->left) { auto prev = curr->left; while (prev->right) { prev = prev->right; } prev->right = curr->right; curr->right = curr->left; curr->left = nullptr ; } curr = curr->right; } } };
从前序遍历和中序遍历构造二叉树
105.
从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
根据前序遍历特点,最先遍历的肯定是根节点,所以第一个数一定是根节点,然后根据这个根节点,从中序遍历找到对应的位置,那么中序遍历该位置的左边为左子树的节点,右边为右子树的节点,依次递归。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 var buildTree = function (preorder, inorder ) { function recur (preorder, preLeft, preRight, inorder, inLeft, inRight ) { if (preLeft > preRight) { return null ; } const root = new TreeNode (preorder[preLeft]); const inIndex = inorder.findIndex ((item ) => item === root.val ); const leftLength = inIndex - inLeft, rightLength = inRight - inIndex; root.left = recur ( preorder, preLeft + 1 , preLeft + leftLength, inorder, inLeft, inIndex - 1 ); root.right = recur ( preorder, preLeft + leftLength + 1 , preRight, inorder, inIndex + 1 , inRight ); return root; } return recur (preorder, 0 , preorder.length - 1 , inorder, 0 , inorder.length - 1 ); };
路径总和 Ⅲ
437.
路径总和 III - 力扣(LeetCode)
法一:深度优先搜索,每次计算以root为根节点,向下计算满足targetSum的个数,记为rootSum(root, targetSum),然后递归遍历每个节点,计算以每个节点为根节点的满足条件的个数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 var pathSum = function (root, targetSum ) { if (!root) { return 0 ; } return ( rootSum (root, targetSum) + pathSum (root.left , targetSum) + pathSum (root.right , targetSum) ); }; function rootSum (root, targetSum ) { if (!root) { return 0 ; } return ( rootSum (root.left , targetSum - root.val ) + rootSum (root.right , targetSum - root.val ) + (root.val === targetSum ? 1 : 0 ) ); }
法二:前缀和
从root节点到node节点的路径上的和记为前缀和,可以看作是一维的前缀和。
使用前序遍历,遍历过程中记录前缀和,同时记录满足该前缀和的节点个数。
如果root到node之间的节点p满足prefixSum - targetSum,则说明p节点的下一个节点到node节点前缀和为targetSum。
计算完成后恢复,因为计算其他路径的前缀和时可能有相同的前缀和,但是其他路径的会影响当前路径,因此需要删除。参考:题解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 var pathSum = function (root, targetSum ) { if (!root) { return 0 ; } const prefix = new Map (); prefix.set (0 , 1 ); return dfs (root, prefix, 0 , targetSum); }; function dfs (root, prefix, curr, targetSum ) { if (!root) { return 0 ; } curr += root.val ; let ret = prefix.get (curr - targetSum) ?? 0 ; prefix.set (curr, (prefix.get (curr) ?? 0 ) + 1 ); ret += dfs (root.left , prefix, curr, targetSum); ret += dfs (root.right , prefix, curr, targetSum); prefix.set (curr, prefix.get (curr) - 1 ); return ret; }
二叉树的最近公共祖先
236.
二叉树的最近公共祖先 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 var lowestCommonAncestor = function (root, p, q ) { if (!root || root === p || root === q) { return root; } const left = lowestCommonAncestor (root.left , p, q); const right = lowestCommonAncestor (root.right , p, q); if (!left) { return right; } if (!right) { return left; } return root; };
二叉树中的最大路径和
124.
二叉树中的最大路径和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
采用递归的方式,设置maxGain(root)函数,表示从从root节点上能获得的最大贡献值,贡献值表示为从root节点向左子树或者右子树延申(只能是root的左子树或者右子树一个方向),得到的最大的值,以此类推,roo.left的最大贡献值表示为root.left向左子树或者右子树延申。这是一个递归的过程。
可以在递归的时候求出最大的路径和。当左子树和右子树的最大贡献值大于 0
的时候,才能算作贡献去计算路径和,否则还不如直接使用根节点当作单独的路径和大。最后返回贡献值,选择左右子树最大的作为贡献值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 var maxPathSum = function (root ) { let maxSum = -Infinity ; function maxGain (root ) { if (!root) { return 0 ; } const leftGain = Math .max (maxGain (root.left ), 0 ); const rightGain = Math .max (maxGain (root.right ), 0 ); const temp = root.val + leftGain + rightGain; console .log (maxSum); maxSum = Math .max (maxSum, temp); return root.val + Math .max (leftGain, rightGain); } maxGain (root); return maxSum; };
岛屿数量
200.
岛屿数量 - 力扣(LeetCode)
使用深度优先遍历,遇到1后进行深度优先遍历,将遍历到的所有1进行标记,组成岛屿。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 var numIslands = function (grid ) { const m = grid.length , n = grid[0 ].length ; const visited = new Array (m).fill (null ).map ((item ) => new Array (n).fill (false )); const dx = [0 , 1 , 0 , -1 ], dy = [1 , 0 , -1 , 0 ]; function dfs (grid, x, y ) { visited[x][y] = true ; for (let i = 0 ; i < dx.length ; i++) { const nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i]; if ( nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= m || ny >= n || grid[nx][ny] === '0' || visited[nx][ny] ) { continue ; } dfs (grid, nx, ny); } } let ans = 0 ; for (let i = 0 ; i < grid.length ; i++) { for (let j = 0 ; j < grid[i].length ; j++) { if (grid[i][j] === '1' && !visited[i][j]) { dfs (grid, i, j); ans++; } } } return ans; };
腐烂的橘子
994.
腐烂的橘子 - 力扣(LeetCode)
多源的宽度优先搜索,因为可能同时存在多个腐烂的橘子,是同时扩散的。
初始时找到所有腐烂的橘子加入队列,作为初始的多个起点,然后遍历,同时这里使用了102.
二叉树的层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode) 的方法,每一次遍历“一层”。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 var orangesRotting = function (grid ) { const m = grid.length , n = grid[0 ].length ; const que = []; let cnt = 0 ; for (let i = 0 ; i < grid.length ; i++) { for (let j = 0 ; j < grid[i].length ; j++) { grid[i][j] === 2 && que.push ([i, j]); grid[i][j] === 1 && cnt++; } } const dx = [0 , 1 , 0 , -1 ], dy = [1 , 0 , -1 , 0 ]; let ans = 0 ; while (que.length && cnt) { ans++; let size = que.length ; while (size--) { const [x, y] = que.shift (); for (let i = 0 ; i < dx.length ; i++) { const nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i]; if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= m || ny >= n || grid[nx][ny] !== 1 ) { continue ; } cnt--; grid[nx][ny] = 2 ; que.push ([nx, ny]); } } } return cnt === 0 ? ans : -1 ; };
课程表
207.
课程表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
拓扑排序,首先是图的构造,使用二维数组表示,graph[i] = [a, b, c]表示i指向a, b, c。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 var canFinish = function (numCourses, prerequisites ) { const graph = new Array (numCourses).fill (null ).map ((item ) => []); const indegree = new Array (numCourses).fill (0 ); for (const [a, b] of prerequisites) { graph[b].push (a); indegree[a]++; } const que = []; for (let i = 0 ; i < numCourses; i++) { indegree[i] === 0 && que.push (i); } while (que.length ) { const i = que.shift (); for (const j of graph[i]) { indegree[j]--; indegree[j] === 0 && que.push (j); } } for (let i = 0 ; i < numCourses; i++) { if (indegree[i] !== 0 ) { return false ; } } return true ; };
实现 Trie 树
208.
实现 Trie (前缀树) - 力扣(LeetCode)
每个节点(假设)有 26
个子树(根据字符集决定),每个边表示一个字符,如果有这个边,表示存在,没有边表示不存在。
如果需要判断每个单词出现了多少次,或者是以某个单词为前缀的单词有多少个,可以增加变量
end: int, pass: int用数量表示
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 var Trie = function ( this .next = new Map (); this .end = false ; }; Trie .prototype insert = function (word ) { let temp = this ; for (let i = 0 ; i < word.length ; i++) { const c = word[i]; if (!temp.next .get (c)) { temp.next .set (c, new Trie ()); } temp = temp.next .get (c); } temp.end = true ; }; Trie .prototype search = function (word ) { let temp = this ; for (let c of word) { const node = temp.next .get (c); if (!node) { return false ; } temp = node; } return temp.end ; }; Trie .prototype startsWith = function (prefix ) { let temp = this ; for (let c of prefix) { const node = temp.next .get (c); if (!node) { return false ; } temp = node; } return true ; };
全排列
46.
全排列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目中限定了没有重复的元素,递归时无需特判。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 var permute = function (nums ) { const ans = []; function dfs (nums, k ) { if (nums.length === k) { ans.push (nums.slice ()); return ; } for (let i = k; i < nums.length ; i++) { [nums[i], nums[k]] = [nums[k], nums[i]]; dfs (nums, k + 1 ); [nums[i], nums[k]] = [nums[k], nums[i]]; } } dfs (nums, 0 ); return ans; };
子集
78.
子集 - 力扣(LeetCode)
求子集,核心思想可以用二进制考虑,每一个元素都有“要”或者“不要”两种选择,可以采用递归的方式,也可以采用迭代使用二进制方式,二进制的某位为
1 时表示要,0 表示不要。
使用回溯方式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 var subsets = function (nums ) { const ans = []; function dfs (k, ret ) { if (k === nums.length ) { ans.push (ret.slice ()); return ; } dfs (k + 1 , ret); ret.push (nums[k]); dfs (k + 1 , ret); ret.pop (); } dfs (0 , []); return ans; };
使用二进制方式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 var subsets = function (nums ) { const ans = []; for (let i = 0 ; i < 1 << nums.length ; i++) { const ret = []; for (let j = 0 ; j < nums.length ; j++) { if (i & (1 << j)) { ret.push (nums[j]); } } ans.push (ret); } return ans; };
电话号码的字母组合
17.
电话号码的字母组合 - 力扣(LeetCode)
也是一种组合问题,但是较为简单,给定一个一组数字字符串,按照这个顺序打出来的字母组合有哪些,因为数字顺序时固定的,可以每次从当前数字中挑一个对应的字母添加到结果末尾,然后选择下一个数字的字母,依次类推。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 var letterCombinations = function (digits ) { if (digits.length === 0 ) { return []; } const numDigit = { 2 : ['a' , 'b' , 'c' ], 3 : ['d' , 'e' , 'f' ], 4 : ['g' , 'h' , 'i' ], 5 : ['j' , 'k' , 'l' ], 6 : ['m' , 'n' , 'o' ], 7 : ['p' , 'q' , 'r' , 's' ], 8 : ['t' , 'u' , 'v' ], 9 : ['w' , 'x' , 'y' , 'z' ], }; const ans = []; function dfs (k, ret ) { if (k === digits.length ) { ans.push (ret); return ; } for (let c of numDigit[digits[k]]) { dfs (k + 1 , ret.concat (c)); } } dfs (0 , '' ); return ans; };
组合总和
39.
组合总和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难点在于结果集不能重复,如[2, 2, 3]和[2, 3, 2]是重复的。因此在
dfs
时需要主动避免产生重复的结果。做法:每次搜索时设置下一次搜索的起点,避免后续的搜索会搜索前边搜索过的结果。
具体可参考:39.
组合总和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 var combinationSum = function (candidates, target ) { const ans = []; function dfs (ret, sum, idx ) { if (idx === candidates.length ) { return ; } if (sum === target) { ans.push (ret.slice ()); return ; } dfs (ret, sum, idx + 1 ); if (sum + candidates[idx] <= target) { ret.push (candidates[idx]); dfs (ret, sum + candidates[idx], idx); ret.pop (); } } dfs ([], 0 , 0 ); return ans; };
括号生成
22.
括号生成 - 力扣(LeetCode)
多种方法可以做,这里先采取回溯法做。
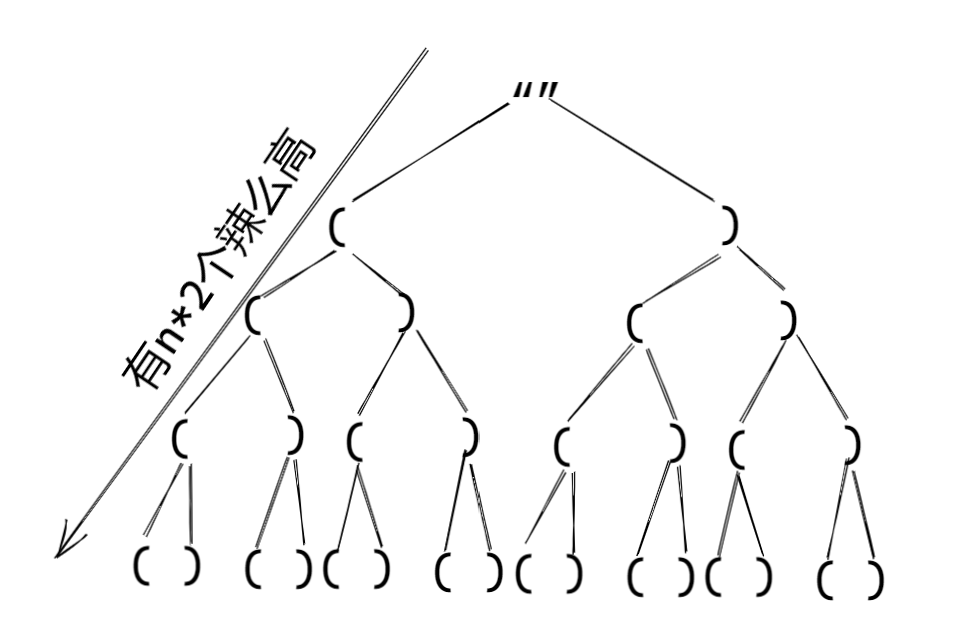
回溯的前提是使用深度优先搜索,然后使用剪枝策略优化。因此首先想到使用深搜搜索出所有的结果。画出递归树:
通过递归树可以看到,有些结果是不能要的,比如((((、))))等等,因此,在进行深搜时需要加上判断条件进行剪枝。
如果括号能匹配,首先左括号的个数不能超过 n,因为这里是从前往后追加括号,因此左括号的个数优先增大,而且,如果想要后续的右括号可以匹配上左括号,左括号的个数一定要大于或等于右括号 ,否则像(())),后续无论怎么追加括号,都不是合法的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 var generateParenthesis = function (n ) { const ans = []; const path = []; function dfs (left, right ) { if (left > n || left < right) { return ; } if (path.length === 2 * n) { ans.push (path.join ('' )); return ; } path.push ('(' ); dfs (left + 1 , right); path.pop (); path.push (')' ); dfs (left, right + 1 ); path.pop (); } dfs (0 , 0 ); return ans; };
单词搜索
79.
单词搜索 - 力扣(LeetCode)
此题需要用回溯才能达到最佳,因此要考虑剪枝策略。
首先按照深搜的方式,从某个点出发,遍历所有方向所有长度的字符串,直到找到符合条件的。
可以想到一个剪枝策略,当下一个字符和要查找的字符串的下一个字符匹配时才进行搜索,如果不匹配,即使搜索了,也是不满足的。
还有一个注意点,停止条件是:遍历到word字符串的最后一个位置时就要终止递归了。
因为dfs(i, j, idx)表示的是:board[i, j]位置的字符和word[idx]位置的字符相同,只有当相同的时候才会走进这个递归。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 var exist = function (board, word ) { const m = board.length , n = board[0 ].length ; const visited = new Array (m).fill (null ).map ((item ) => new Array (n).fill (false )); const dx = [0 , 1 , 0 , -1 ], dy = [1 , 0 , -1 , 0 ]; let ans = false ; function dfs (x, y, idx ) { if (idx === word.length - 1 ) { ans = true ; return ; } if (ans) { return ; } visited[x][y] = true ; for (let i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { const nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i]; if ( nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && !visited[nx][ny] && board[nx][ny] == word[idx + 1 ] ) { visited[nx][ny] = true ; dfs (nx, ny, idx + 1 ); visited[nx][ny] = false ; } } visited[x][y] = false ; } for (let i = 0 ; i < board.length ; i++) { for (let j = 0 ; j < board[i].length ; j++) { board[i][j] === word[0 ] && dfs (i, j, 0 ); } } return ans; };
分割回文串
131.
分割回文串 - 力扣(LeetCode)
用到了两种算法,一种是动态规划,一种是回溯。
回溯用于搜索到所有可能的子串,然后通过动态规划判断是否可以组成回文串。
使用一个下标i表示当前搜索到的位置,[0, i - 1]表示已经搜索过的,[i, n]表示没有搜索的,然后对[i, j]进行判断,如果可以构成回文串,则从j + 1开始进行下一次搜索。
动态规划主要用于快速判断是否是回文串,这里采用记忆化搜索的方式。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 var partition = function (s ) { const ans = []; const f = new Array (s.length ).fill (null ).map ((item ) => new Array (s.length ).fill (null )); function dfs (i, ret ) { if (i === s.length ) { ans.push (ret.slice ()); return ; } for (let j = i; j < s.length ; j++) { if (dp (i, j)) { ret.push (s.slice (i, j + 1 )); dfs (j + 1 , ret); ret.pop (); } } } function dp (x, y ) { if (f[x][y] !== null ) { return f[x][y]; } for (let i = x, j = y; i < j; i++, j--) { if (s[i] !== s[j]) { f[x][y] = false ; return false ; } } f[x][y] = true ; return true ; } dfs (0 , []); return ans; };
N 皇后
51.
N 皇后 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难点在于怎么快速判断当前位置是否是可放的位置,即判断当前位置的行、列和两个对角线是否有其他皇后。
其中表示两个对角线是最难的。
可以将行和列看作是坐标系 ,将对角线平移的时候,和y轴的交点即为在数组中的下标,需要注意的是另一种情况下标会出现负数,因此可以将整体加上n - 1保证为正数,或者也可以使用哈希表存储不用考虑正负问题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 var solveNQueens = function (n ) { const row = new Array (n).fill (false ), col = row.slice (); const diag = new Array (2 * n - 1 ), rediag = diag.slice (); const ans = []; const place = new Array (n).fill (null ).map ((item ) => new Array (n).fill ('.' )); function dfs (idx ) { if (idx === n) { ans.push (place.map ((item ) => item.join ('' ))); return ; } for (let i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (check (idx, i)) { row[idx] = col[i] = diag[idx + i] = rediag[idx - i + n - 1 ] = true ; place[idx][i] = 'Q' ; dfs (idx + 1 ); place[idx][i] = '.' ; row[idx] = col[i] = diag[idx + i] = rediag[idx - i + n - 1 ] = false ; } } } function check (idx, i ) { return !(row[idx] || col[i] || diag[idx + i] || rediag[idx - i + n - 1 ]); } dfs (0 ); return ans; };
搜索插入位置
35.
搜索插入位置 - 力扣(LeetCode)
二分查找的题,记住这个二分经典模板即可。
二分经典模板即可解决这道题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 var searchInsert = function (nums, target ) { let left = 0 , right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left <= right) { const mid = (left + right) >> 1 ; if (nums[mid] === target) { return mid; } if (nums[mid] > target) { right = mid - 1 ; } else { left = mid + 1 ; } } return left; };
搜索二维矩阵
74.
搜索二维矩阵 - 力扣(LeetCode)
二维矩阵的搜索,从二分角度考虑,要寻找中间值,从题目中的排序规律可以看到,右上角 的值处于中间位置,向左减小,向下增大。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 var searchMatrix = function (matrix, target ) { let x = 0 , y = matrix[0 ].length - 1 ; while (x < matrix.length && y >= 0 ) { if (matrix[x][y] === target) { return true ; } else if (matrix[x][y] > target) { y--; } else { x++; } } return false ; };
排序数组中查找第一个和最后一个位置
34.
在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置 - 力扣(LeetCode)
模板返回大于等于 某个值的最小下标、小于等于 某个值的最大下标。
结果需要注意特殊情况,如果大于等于 的时候,当返回的结果是nums.length时,表示数组为空或者所有的值都小于target。如果小于等于 的时候,返回的结果是-1时,表示数组为空或者所有的值都大于target。
当大于等于的时候最终的left为结果,小于等于的时候最终的right为结果。
只记住大于等于 的模板即可,反过来的可以类比一下推出来。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 var searchRange = function (nums, target ) { function biSearch (nums, target, type ) { let left = 0 , right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left <= right) { const mid = (left + right) >> 1 ; if (type === 0 ) { if (nums[mid] >= target) { right = mid - 1 ; } else { left = mid + 1 ; } } else { if (nums[mid] <= target) { left = mid + 1 ; } else { right = mid - 1 ; } } } return type === 0 ? left : right; } const start = biSearch (nums, target, 0 ); if (start === nums.length || nums[start] !== target) { return [-1 , -1 ]; } const end = biSearch (nums, target, 1 ); return [start, end]; };
搜索旋转排序数组
33.
搜索旋转排序数组 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 var search = function (nums, target ) { if (nums.length === 0 ) { return -1 ; } let left = 0 , right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left <= right) { const mid = (left + right) >> 1 ; if (nums[mid] === target) { return mid; } if (nums[left] <= nums[mid]) { if (nums[left] <= target && target < nums[mid]) { right = mid - 1 ; } else { left = mid + 1 ; } } else { if (nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[right]) { left = mid + 1 ; } else { right = mid - 1 ; } } } return -1 ; };
寻找旋转排序数组中的最小值
153.
寻找旋转排序数组中的最小值 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目中给定的数组和上一题一样,依然是使用二分,这里和最后一个值进行比较,因为旋转后的最后一个值,是第二段区间的最大值,第一段区间的最小值。
注意返回的是 **left**,可以按照“返回没有等号的那个被赋值的变量”,如 **nums[mid] > nums[nums.length - 1]**条件中没有 **=**,则返回 **left**。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 var findMin = function (nums ) { let left = 0 , right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left <= right) { const mid = (left + right) >> 1 ; if (nums[mid] > nums[nums.length - 1 ]) { left = mid + 1 ; } else { right = mid - 1 ; } } return nums[left]; };
寻找两个正序数组的中位数
4.
寻找两个正序数组的中位数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
要求O(log(m + 1))的复杂度,可以将问题转化为,两个正序数组中,寻找第k小的数,最多寻找两次即可寻找到两个中位数的位置。
具体可参考题解:4.
寻找两个正序数组的中位数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 var findMedianSortedArrays = function (nums1, nums2 ) { const sumLen = nums1.length + nums2.length ; function findKthSmallest (nums1, start1, end1, nums2, start2, end2, k ) { const len1 = end1 - start1 + 1 , len2 = end2 - start2 + 1 ; if (len1 > len2) return findKthSmallest (nums2, start2, end2, nums1, start1, end1, k); if (len1 === 0 ) return nums2[start2 + k - 1 ]; if (k === 1 ) return Math .min (nums1[start1], nums2[start2]); const i = start1 + Math .min (Math .floor (k / 2 ), len1) - 1 ; const j = start2 + Math .min (Math .floor (k / 2 ), len2) - 1 ; if (nums1[i] < nums2[j]) { return findKthSmallest ( nums1, i + 1 , end1, nums2, start2, end2, k - (i - start1 + 1 ) ); } else { return findKthSmallest ( nums1, start1, end1, nums2, j + 1 , end2, k - (j - start2 + 1 ) ); } } if (sumLen % 2 === 0 ) { return ( (findKthSmallest ( nums1, 0 , nums1.length - 1 , nums2, 0 , nums2.length - 1 , Math .ceil (sumLen / 2 ) ) + findKthSmallest ( nums1, 0 , nums1.length - 1 , nums2, 0 , nums2.length - 1 , Math .ceil (sumLen / 2 ) + 1 )) / 2 ); } else { return findKthSmallest ( nums1, 0 , nums1.length - 1 , nums2, 0 , nums2.length - 1 , Math .ceil (sumLen / 2 ) ); } };
最小栈
155.
最小栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)
方法一:使用辅助栈
每次入栈时,使用另一个栈保存当前栈里的最小值,同步出入栈,会有额外的空间。
🍕 方法二:不适用额外空间,栈里保存的是每次入栈的值和最小值的差。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 var MinStack = function ( this .stk = []; this .minValue = -Infinity ; }; MinStack .prototype push = function (val ) { if (!this .stk .length ) { this .stk .push (0 ); this .minValue = val; } else { const diff = val - this .minValue ; this .stk .push (diff); this .minValue = diff > 0 ? this .minValue : val; } }; MinStack .prototype pop = function ( if (this .stk .length ) { const diff = this .stk .pop (); if (diff > 0 ) { const top = diff + this .minValue ; } else { const top = this .minValue ; this .minValue = top - diff; } } }; MinStack .prototype top = function ( if (this .stk .length ) { const diff = this .stk .at (-1 ); return diff > 0 ? diff + this .minValue : this .minValue ; } }; MinStack .prototype getMin = function ( return this .minValue ; };
字符串解码
394.
字符串解码 - 力扣(LeetCode)
方法 1
根据规则,可以看作是一个递归的过程,递归调用。
用栈是为了匹配括号,首先匹配到最外层的括号,然后对括号内的字符串进行递归调用解码。
需要注意:数字和括号的前后都可能存在不需要解码的字符串,仍然需要拼接到结果中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 var decodeString = function (s ) { let ans = '' ; const stk = []; let start = 0 ; for (let i = 0 ; i < s.length ; i++) { if (s[i] === '[' ) { stk.push (i); } else if (s[i] === ']' ) { if (stk.length === 1 ) { const idx = stk.pop (); let j = idx - 1 ; while (j >= 0 && '0' <= s[j] && s[j] <= '9' ) j--; j++; const cnt = Number (s.slice (j, idx)); ans = ans .concat (s.slice (start, j)) .concat (decodeString (s.slice (idx + 1 , i)).repeat (cnt)); start = i + 1 ; } else { stk.pop (); } } } if (start !== s.length ) { ans = ans.concat (s.slice (start)); } return ans || s; };
方法 2
按顺序依次遍历,栈中存储要循环的次数以及当前循环之前 的结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 var decodeString = function (s ) { const arr = [...s]; let ans = []; const stk = []; let cnt = 0 ; for (let i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i++) { if (arr[i] <= '9' && arr[i] >= '0' ) { cnt = cnt * 10 + Number (arr[i]); } else if (arr[i] === '[' ) { stk.push ([cnt, ans.slice ()]); cnt = 0 ; ans = []; } else if (arr[i] === ']' ) { const [multi, ret] = stk.pop (); ret.push (...[...ans.join ('' ).repeat (multi)]); ans = ret; } else { ans.push (arr[i]); } } return ans.join ('' ); };
每日温度
739.
每日温度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
使用单调栈, 栈底到栈顶元素依次递减。只要元素在栈中,就说明目前没有发现后续有比该元素大的。
栈里存储的是元素下标,方便计算差了多少天。
如果栈空,直接入栈
否则,如果元素比栈顶元素大,说明栈顶元素后的第一个大的就是当前元素,取出来,计算差值。
否则,跳过直接加入到栈中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 var dailyTemperatures = function (temperatures ) { const stk = [], ans = new Array (temperatures.length ).fill (0 ); for (let i = 0 ; i < temperatures.length ; i++) { while (stk.length && temperatures[stk.at (-1 )] < temperatures[i]) { const t = stk.pop (); ans[t] = i - t; } stk.push (i); } return ans; };
数组中第 K 个最大的元素
215.
数组中的第 K 个最大元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
要求用O(n)的复杂度,数学证明快速选择 算法为O(n)复杂度,因此直接使用即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 var findKthLargest = function (nums, k ) { function quickChoice (nums, left, right, k ) { if (left >= right) return nums[left]; let less = left - 1 , i = left, more = right + 1 ; const x = nums[Math .floor ((left + right) / 2 )]; while (i < more) { if (nums[i] < x) { less++; [nums[i], nums[less]] = [nums[less], nums[i]]; i++; } else if (nums[i] > x) { more--; [nums[i], nums[more]] = [nums[more], nums[i]]; } else { i++; } } if (less < k && k < more) return nums[k]; if (k <= less) return quickChoice (nums, left, less, k); if (k >= more) return quickChoice (nums, more, right, k); } return quickChoice (nums, 0 , nums.length - 1 , nums.length - k); };
前 K 个高频元素
347.
前 K 个高频元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目要求复杂度优于O(nlogn),前 K
个元素很容易联想到堆这种数据结构。
要求频率大小,首先可以遍历数组求出每个元素出现的次数,然后用大小为K
的小根堆 存储次数,使用小根堆原因是:如果新元素大于堆顶,说明在已知的前
K 个元素中,新元素能把堆顶元素踢掉(堆顶肯定不是前 K
个了),剩余的元素都大于堆顶。直到遍历完所有的频率次数组合。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 var topKFrequent = function (nums, k ) { const numCnt = new Map (); for (const num of nums) { if (numCnt.has (num)) { numCnt.set (num, numCnt.get (num) + 1 ); } else { numCnt.set (num, 1 ); } } const heap = []; const fn = (parent, son ) => { return parent.cnt - son.cnt ; }; for (const [num, cnt] of numCnt) { if (heap.length < k) { heap.push ({ num, cnt }); heapUp (heap, heap.length - 1 , fn); } else if (heap[0 ].cnt < cnt) { heap[0 ] = { num, cnt }; heapDown (heap, 0 , k, fn); } } return heap.map ((item ) => item.num ); }; function heapUp (arr, idx, fn ) { let parentIdx; while (fn (arr[(parentIdx = Math .trunc ((idx - 1 ) / 2 ))], arr[idx]) > 0 ) { swap (arr, parentIdx, idx); idx = parentIdx; } } function heapDown (arr, idx, size, fn ) { let t = idx, left = 2 * idx + 1 , right = 2 * idx + 2 ; if (left < size && fn (arr[t], arr[left]) > 0 ) { t = left; } if (right < size && fn (arr[t], arr[right]) > 0 ) { t = right; } if (t !== idx) { swap (arr, t, idx); heapDown (arr, t, size, fn); } } function swap (arr, i, j ) { const t = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = t; }
跳跃游戏
55.
跳跃游戏 - 力扣(LeetCode)
贪心算法,如果能到达i,那么从i位置能到达的最远的位置是i + nums[i],记为maxDistance,然后继续向后计算,如果i + 1 <= maxDistance,就说明在上一步的前提下,可以到达i + 1位置,然后基于该位置更新maxDistance。初始时最远位置是
0。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution {public : bool canJump (vector<int >& nums) int maxDistance = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.size (); i++) { if (i <= maxDistance) { maxDistance = max (maxDistance, i + nums[i]); } } return maxDistance >= nums.size () - 1 ; } };
跳跃游戏 Ⅱ
45.
跳跃游戏 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
贪心算法,题目中保证一定可以到最终位置。在位置i时,可以到达的最远位置为i + nums[i],那么是不是应该跳到i + nums[i]位置呢?不一定。从i位置最远可以跳到i + nums[i],如果j位置(i <= j <= i + nums[i]),并且从j位置跳的最远距离在这个区间中时最远的,那么下一步应该跳到j位置,保证下一步跳的最远。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {public : int jump (vector<int >& nums) int maxPos = 0 , ans = 0 , i = 0 ; while (maxPos < nums.size () - 1 ) { int end = 0 ; for (int j = i; j <= maxPos; j++) { end = max (end, j + nums[j]); } i = maxPos; maxPos = end; ans++; } return ans; } };
完全平方数
279.
完全平方数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
动态规划,f[i]表示i这个数的完全平方数的最少数量。
由定义可知,组成i这个数的完全平方数的范围肯定在j在这个区间内,那么如果完全平方数包含j这个数,剩余的数的最少数量则由f[i - j * j]表示,可以看成子问题,使用动态规划做。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 var numSquares = function (n ) { const f = new Array (n + 1 ).fill (Infinity ); f[0 ] = 0 ; for (let i = 1 ; i < f.length ; i++) { for (let j = 1 ; j <= i / j; j++) { f[i] = Math .min (f[i], f[i - j * j] + 1 ); } } return f.at (-1 ); };
零钱兑换
322.
零钱兑换 - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路同上
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 var coinChange = function (coins, amount ) { const f = new Array (amount + 1 ).fill (Infinity ); f[0 ] = 0 ; for (let i = 1 ; i < f.length ; i++) { for (const coin of coins) { if (i >= coin) { f[i] = Math .min (f[i], f[i - coin] + 1 ); } } } return f.at (-1 ) === Infinity ? -1 : f.at (-1 ); };
单词拆分
139.
单词拆分 - 力扣(LeetCode)
动态规划,f[i]表示以前i个字符串能否被表示出来,遍历单词字典,如果前i个字符串的最后的word.size()长度的子字符串和word相等,则说明可以通过word组成,再判断f[i - word.size()]能否组成即可,子问题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 var wordBreak = function (s, wordDict ) { const f = new Array (s.length + 1 ).fill (false ); f[0 ] = true ; for (let i = 1 ; i <= s.length ; i++) { for (const word of wordDict) { if (word.length > i) continue ; if (s.slice (i - word.length , i) === word) { f[i] = f[i - word.length ]; } if (f[i]) break ; } } return f.at (-1 ); };
最长递增子序列
300.
最长递增子序列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
要求O(nlogn)的复杂度,考虑二分查找。
状态定义:f[i]表示长度为i的递增子序列的最后一个元素所有可能的取值的最小值。
根据定义,猜想:f数组是递增的。
反证法:如果f[k] >= f[i]且k = i - 1,那么在以f[i]结尾的子序列中,倒数第二个元素(记为v)一定小于f[i],以v为结尾的子序列长度为k。因为f[i] > v且f[k] >= f[i]所以f[k] > v,与f的定义矛盾。因为长度为k的子序列的最后一个元素是所有可能取值里最小的,初始条件取的f[k]但是推出的结论v < f[k],说明f[k]不是最小,矛盾。
每遍历一个数,从f中求小于num的最大的位置(也就是大于等于num的最小的位置)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {public : int lengthOfLIS (vector<int >& nums) vector<int > f (nums.size() + 1 , 0 ) ; int len = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.size (); i++) { int left = 1 , right = len; while (left <= right) { int mid = left + right >> 1 ; if (f[mid] >= nums[i]) right = mid - 1 ; else left = mid + 1 ; } len = max (len, left); f[left] = nums[i]; } return len; } };
乘积最大子数组
152.
乘积最大子数组 - 力扣(LeetCode)
动态规划,f[i]表示以nums[i]为结尾的子数组的最大乘积,但是这样会出现问题,因为每个元素可能会出现负值,如果是负值,那么期望前一个子数组的乘积越小越好,这与最初定义相反。因此可以维护另一个数组,存储子数组的最小乘积。
maxF[i]表示子数组最大乘积,minF[i]表示子数组最小乘积。
每次遍历时最大值从maxF[i - 1] * nums[i], minF[i - 1] * nums[i], nums[i]中取,最小值同理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution {public : int maxProduct (vector<int >& nums) vector<int > maxF (nums.size(), 0 ) ; vector<int > minF (nums.size(), 0 ) ; maxF[0 ] = minF[0 ] = nums[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.size (); i++) { maxF[i] = max (max (maxF[i - 1 ] * nums[i], minF[i - 1 ] * nums[i]), nums[i]); minF[i] = min (min (minF[i - 1 ] * nums[i], maxF[i - 1 ] * nums[i]), nums[i]); } return *max_element (maxF.begin (), maxF.end ()); } };
分割等和子集
416.
分割等和子集 - 力扣(LeetCode)
可以改造成背包问题,分成两个子集,两个子集的和相等,转化为找一个子集的和恰好为整个数组的和的一半,即选取一些数,这些数的和恰好等于总和的一半。
和原背包不同的是原背包是小于体积 ,这个问题是恰好等于“体积”。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {public : bool canPartition (vector<int >& nums) int sum = 0 ; for (int num : nums) sum += num; if (sum % 2 != 0 ) return false ; vector<vector<bool >> f (nums.size () + 1 , vector <bool >(sum / 2 + 1 , false )); for (int i = 0 ; i < f[0 ].size (); i++) f[0 ][i] = false ; for (int i = 0 ; i < f.size (); i++) f[i][0 ] = true ; for (int j = 1 ; j < f[0 ].size (); j++) { for (int i = 1 ; i < f.size (); i++) { if (nums[i - 1 ] <= j) f[i][j] = f[i - 1 ][j] || f[i - 1 ][j - nums[i - 1 ]]; else f[i][j] = f[i - 1 ][j]; } } return f.back ().back (); } };
最长回文子串
5.
最长回文子串 - 力扣(LeetCode)
如果字符串长度为 1,则肯定是回文串,直接返回,如果字符串长度为
2,则判断两个字符是否相等,如果相等,则返回,否则最长回文子串就是一个字符。
其余情况:
使用f[i][j]表示子串s[i]...s[j]是否是回文子串,是不是回文子串取决于s[i] s[j]是不是相等,如果不相等,则肯定不是回文的,否则判断f[i + 1][j - 1]是不是回文的。
如果f[i + 1][j - 1]是回文的,则f[i][j]是不是回文取决于在前后追加的字符是否相同。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution {public : string longestPalindrome (string s) { const int n = s.size (); if (n == 1 ) return s; if (n == 2 ) return s[0 ] == s[1 ] ? s : string (1 , s[0 ]); vector<vector<bool >> f (n, vector <bool >(n, false )); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { f[i][i] = true ; if (i > 0 ) f[i - 1 ][i] = s[i - 1 ] == s[i]; } for (int len = 3 ; len <= n; len++) { for (int i = 0 ; i + len - 1 < n; i++) { int j = i + len - 1 ; f[i][j] = f[i + 1 ][j - 1 ] && s[i] == s[j]; } } int maxLen = 1 ; int x = 0 , y = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = i; j < n; j++) { if (f[i][j] && maxLen < j - i + 1 ) { maxLen = j - i + 1 ; x = i, y = j; } } } return s.substr (x, maxLen); } };
下一个排列
31.
下一个排列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
按照字典序求下一个排列,题解:31.
下一个排列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
流程:
从后往前找第一个相邻的升序对 (i, j)
在 [j, end)
这个区间中从后向前 寻找第一个 比
nums[i]大的数nums[k]
交换 nums[i] nums[k]
再将 [j, end) 的区间逆序。
总体思路:
将后边较大 的数与前边较小 的数交换,即可以让数值更大。
因为是下一个排列,同时也希望增大 的不是特别快。所以希望较大的数尽量的小。
交换完后,后续的数肯定是降序,反转改成升序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {public : void nextPermutation (vector<int >& nums) if (nums.size () <= 1 ) return ; int i = nums.size () - 2 , j = i + 1 , k = j; for (; i >= 0 ; i--, j--) { if (nums[i] < nums[j]) break ; } if (i >= 0 ) { for (; k >= j; k--) { if (nums[i] < nums[k]) break ; } swap (nums[i], nums[k]); } for (int a = j, b = nums.size () - 1 ; a < b; a++, b--) { swap (nums[a], nums[b]); } } };
寻找重复数
287.
寻找重复数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
看成链表的形式,如果存在重复的数,说明链表中存在环。链表有环判断,通过快慢指针。142. 环形链表
II - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public : int findDuplicate (vector<int >& nums) int fast = 0 , slow = 0 ; while (true ) { fast = nums[nums[fast]]; slow = nums[slow]; if (fast == slow) { slow = 0 ; while (fast != slow) { fast = nums[fast]; slow = nums[slow]; } return slow; } } return 0 ; } };
数据流中的中位数
295.
数据流的中位数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
要求低时间复杂度,根据中位数的定义,使用两个优先队列(堆)存储,一个保存中位数前半部分,一个保存后半部分,加入元素时,判断属于哪一部分,加入完毕后,判断两个队列长度是否相等或者后半部分长度多一个。否则将多的数加入到另一个队列。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class MedianFinder {public : priority_queue<int , vector<int >, less<int >> largeHeap; priority_queue<int , vector<int >, greater<int >> smallHeap; MedianFinder () { } void addNum (int num) if (smallHeap.empty () || num >= smallHeap.top ()) { smallHeap.push (num); if (smallHeap.size () > largeHeap.size () + 1 ) { largeHeap.push (smallHeap.top ()); smallHeap.pop (); } } else { largeHeap.push (num); if (largeHeap.size () > smallHeap.size ()) { smallHeap.push (largeHeap.top ()); largeHeap.pop (); } } } double findMedian () if (smallHeap.size () == largeHeap.size ()) return 1.0 * (smallHeap.top () + largeHeap.top ()) / 2 ; return smallHeap.top (); } };
柱状图中最大的矩形
84.
柱状图中最大的矩形 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution {public : int largestRectangleArea (vector<int >& heights) int n = heights.size (); stack<int > st; vector<int > left (n) , right (n) ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { while (!st.empty () && heights[i] <= heights[st.top ()]) { st.pop (); } left[i] = st.empty () ? -1 : st.top (); st.push (i); } stack <int >().swap (st); for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { while (!st.empty () && heights[i] <= heights[st.top ()]) { st.pop (); } right[i] = st.empty () ? n : st.top (); st.push (i); } int ans = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { ans = max (ans, (right[i] - left[i] - 1 ) * heights[i]); } return ans; } };
最长有效括号
32.
最长有效括号 - 力扣(LeetCode)
f[i]表示以i位置为结尾的最长有效括号长度。
如果s[i] == '('则肯定不是有效括号
如果s[i] == ')',则如果s[i - 1] == '(',最后两个元素可以构成有效括号,再加上f[i - 2]的长度即可。则如果s[i - 1] == ')',判断s[i - f[i - 1] - 1] == '('(判断以s[i - 1]结尾的有效长度的上一个位置是否是左括号),相等的话,则说明[i - f[i - 1] - 1], i]的范围内,两边可以组成括号,中间内部能否组成由f[i - 1]决定,最后加上f[i - f[i - 1] - 2]的长度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution {public : int longestValidParentheses (string s) if (s.size () == 0 ) return 0 ; vector<int > f (s.size(), 0 ) ; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.size (); i++) { if (s[i] == '(' ) continue ; if (i > 0 && s[i - 1 ] == '(' ) { f[i] = i > 1 ? f[i - 2 ] + 2 : 2 ; } else if (i > 0 && s[i - 1 ] == ')' ) { if (i - f[i - 1 ] - 1 >= 0 && s[i - f[i - 1 ] - 1 ] == '(' ) { f[i] = f[i - 1 ] + (i - f[i - 1 ] - 2 >= 0 ? f[i - f[i - 1 ] - 2 ] : 0 ) + 2 ; } } } return *max_element (f.begin (), f.end ()); } };